ASP.NET 路由系统通过注册的路由表旨在实现两个“方向”的路有功能,即针对入栈请求的路由和出栈URL的生成。前者通过调用代表全局路由表的RouteCollection对象的GetRouteData方法实现,后者则依赖于RouteCollection的GetVirtualPathData方法,而最终还是落在继承自RouteBase的路由对象的同名方法的调用上。为了编程的方面,ASP.NET MVC为了设计了HtmlHelper和UrlHelper这两个帮助类,我们可以通过调用它们的ActionLink/RouteLink和Action/RouteUrl根据注册的路有规则生成链接或者URL。从本质上讲,HtmlHelper/UrlHelper实现的对URL的生成最终还是依赖于上面所说的GetVirtualPathData方法。
目录
一、UrlHelper V.S. HtmlHelper
二、UrlHelper.Action V.S. HtmlHelper.ActionLink
三、实例演示:创建一个RouteHelper模拟UrlHelper的URL生成逻辑
四、UrlHelper.RouteUrl V.S. HtmlHelper.RouteLink
一、UrlHelper V.S. HtmlHelper
在介绍如果通过HtmlHelper和UrlHelper来生成链接或者URL之前,我们来先来看看它们的基本定义。从下面给出的代码片断我们可以看出UrlHelper对象实际上对一个表示请求上下文的RequestContext和路由对象集合的RouteCollection对象的封装。它们分别对应于只读属性RequestContext和RouteCollection,并且在构造函数中被初始化。如果在构造UrlHelper的时候没有指定RouteCollection对象,那么通过RouteTable的静态属性Routes表示的全局路有表将直接被使用。
1: public class UrlHelper 2: { 3: //其他成员 4: public UrlHelper(RequestContext requestContext); 5: public UrlHelper(RequestContext requestContext, RouteCollection routeCollection); 6: 7: public RequestContext RequestContext { get; } 8: public RouteCollection RouteCollection { get;} 9: }
再来看看如下所示的HtmlHelper的定义,它同样具有一个表示路由对象集合的RouteCollection属性。和UrlHelper一样,如果在构造函数没有显示指定,那么RouteTable的静态属性Routes表示的RouteCollection对象将会用于初始化该属性。
1: public class HtmlHelper 2: { 3: //其他成员 4: public HtmlHelper(ViewContext viewContext, IViewDataContainer viewDataContainer); 5: public HtmlHelper(ViewContext viewContext, IViewDataContainer viewDataContainer, RouteCollection routeCollection); 6: 7: public RouteCollection RouteCollection { get; } 8: public ViewContext ViewContext { get; } 9: } 10: public class ViewContext : ControllerContext 11: { 12: //省略成员 13: } 14: public class ControllerContext 15: { 16: //其他成员 17: public RequestContext RequestContext { get; set; } 18: public virtual RouteData RouteData { get; set; } 19: }
由于HtmlHelper只要在View中使用,所以它具有一个通过ViewContext属性表示的针对View的上下文。至于该属性对应的类型ViewContext,它是表示Controller上下文的ControllerContext的子类,而后者通过RequestContext和RouteData属性提供当前的请求上下文和路由数据(其实RouteData属性表示的RouteData对象已经包含在RequestContext属性表示的RequestContext对象中)。
二、UrlHelper.Action V.S. HtmlHelper.ActionLink
UrlHelper和HtmlHelper分别通过Action和ActionLink方法用于生成一个针对某个Controller的某个Action的URL和链接。下面的代码片断列出了UrlHelper的所有Action重载,参数actionName和controllerName分别代表Action和Controller的名称。通过object或者RouteValueDictionary类型表示的routeValues参数表示替换URL模板中变量的变量值。参数protocol和hostName代表作为完整URL的传输协议(比如http和https等)以及主机名。
1: public class UrlHelper 2: { 3: //其他成员 4: public string Action(string actionName); 5: public string Action(string actionName, object routeValues); 6: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName); 7: public string Action(string actionName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 8: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues); 9: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 10: 11: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues, string protocol); 12: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, string protocol, string hostName); 13: }
对于定义在UrlHelper中的众多Action方法,如果我们显示指定了传输协议(protocol参数)或者主机名称,返回的是一个完整的URL;否则返回的是一个相对URL。如果我们没有显示地指定Controller的名称(controllerName参数),那么当前Controller的名称被采用。对于UrlHelper来说,通过RequestContext属性表示的当前请求上下文包含了相应的路由信息,即RequestContext的RouteData属性表示的RouteData。RouteData的Values属性中必须包含一个Key为“controller”的元素,其值就代表当前Controller的名称。
在System.Web.Mvc.Html.LinkExtensions中,我们为HtmlHelper定义了如下所示的一系列ActionLink方法重载。顾名思义,ActionLink不再仅仅返回一个URL,而是生成一个链接(...),但是其中作为目标URL的生成逻辑和UriHelper是完全一致的。
1: public static class LinkExtensions 2: { 3: //其他成员 4: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName); 5: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, object routeValues); 6: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, string controllerName); 7: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 8: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 9: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, IDictionary<string, object> htmlAttributes); 10: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 11: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, string controllerName,RouteValueDictionary routeValues, IDictionary<string, object> htmlAttributes); 12: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, string controllerName, string protocol, string hostName, string fragment, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 13: public static MvcHtmlString ActionLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string actionName, string controllerName, string protocol, string hostName, string fragment, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, IDictionary<string, object> htmlAttributes); 14: }
三、实例演示:创建一个RouteHelper模拟UrlHelper的URL生成逻辑
为了让读者对UrlHelper如果利用ASP.NET路由系统进行URL生成的逻辑具有一个深刻认识,我们接下来创建一个名为RouteHelper的等效帮助类。我们将RouteHelper定义在创建的一个ASP.NET Web应用中,如下面的代码片断所示,RouteHelper具有RequestContext和RouteCollection两个属性,前者在构造函数中指定,后者则只是使用通过RouteTable的Routes静态属性表示的全局路由表。源代码从这里下载。
1: public class RouteHelper 2: { 3: public RequestContext RequestContext { get; private set; } 4: public RouteCollection RouteCollection { get; private set; } 5: public RouteHelper(RequestContext requestContext) 6: { 7: this.RequestContext = requestContext; 8: this.RouteCollection = RouteTable.Routes; 9: } 10: 11: public string Action(string actionName) 12: { 13: return this.Action(actionName, null, null, null, null); 14: } 15: public string Action(string actionName, object routeValues) 16: { 17: return this.Action(actionName, null, 18: new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues), null, null); 19: } 20: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName) 21: { 22: return this.Action(actionName, controllerName, null, null, null); 23: } 24: public string Action(string actionName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) 25: { 26: return this.Action(actionName, null, routeValues, null, null); 27: } 28: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues) 29: { 30: return this.Action(actionName, controllerName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues), null, null); 31: } 32: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues) 33: { 34: return this.Action(actionName, controllerName, routeValues, null, null); 35: } 36: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, object routeValues, string protocol) 37: { 38: return this.Action(actionName, controllerName, new RouteValueDictionary(routeValues), protocol, null); 39: } 40: public string Action(string actionName, string controllerName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, string protocol, string hostName) 41: { 42: controllerName = controllerName ?? (string)this.RequestContext.RouteData.Values["controller"]; 43: routeValues = routeValues ?? new RouteValueDictionary(); 44: routeValues.Add("action", actionName); 45: routeValues.Add("controller", controllerName); 46: string virtualPath = this.RouteCollection.GetVirtualPath(this.RequestContext, routeValues).VirtualPath; 47: if (string.IsNullOrEmpty(protocol) && string.IsNullOrEmpty(hostName)) 48: { 49: return virtualPath.ToLower(); 50: } 51: 52: protocol = protocol??"http"; 53: Uri uri = this.RequestContext.HttpContext.Request.Url; 54: hostName = hostName ?? uri.Host + ":" + uri.Port; 55: return string.Format("{0}://{1}{2}", protocol, hostName, virtualPath).ToLower(); 56: } 57: }
RouteHelper具有与UriHelper完全一致的Action方法重载定义,而URL的生成最终体现在最后一个Action重载中。具体的逻辑很简单,如果指定的Controller名称为Null,我们通过RequestContext获取出当前Controller名称,然后将Action和Controller名称添加到表示路由变量 列表的RouteValueDictionary对象中(routeValues参数),对应的Key分别是“action”和“controller”。
然后我们调用RouteCollection的GetVirtualPath得到一个VirtualPathData对象。如果既没有显示指定传输协议名称也没有指定主机名称,直接返回VirtualPathData的VirtualPath体现的相对路径,否则生成一个完整的URL。如果没有指定主机名称,我们采用当前请求的主机名称,并且使用当前的端口;如果没有指定传输协议,则直接使用“http”。
接下来我们在添加的Global.asax中通过如下的代码注册一个URL模板为"{controller}/{action}/{id}”的路由对象。
1: public class Global : System.Web.HttpApplication 2: { 3: protected void Application_Start(object sender, EventArgs e) 4: { 5: RouteTable.Routes.MapRoute("default", "{controller}/{action}/{id}"); 6: } 7: }
在添加的Web页面(Default.aspx)中我们通过如下的代码利用我们自定义的RouteHelper生成三个URL。在页面加载事件处理方法中,我们根据手工创建的HttpRequest和HttpResponse创建一个HttpContext对象,并进一步创建HttpContextWrapper对象。然后我们手工创建一个RouteData对象,并针对上面定义的URL模板添加了三个变量元素(controller=home;action=index;id=002),它们实际上和我们创建的HttpRequest的URL是一一匹配的。最后针对创建的HttpContextWrapper对象和RouteData进一步创建RequestContext对象,并最终创建出RouteHelper对象。
1: public partial class Default : System.Web.UI.Page 2: { 3: protected void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e) 4: { 5: HttpRequest request = new HttpRequest("default.aspx", "", null); 6: HttpResponse response = new HttpResponse(new StringWriter()); 7: HttpContext context = new HttpContext(request, response); 8: HttpContextBase contextWrapper = new HttpContextWrapper(context); 9: 10: RouteData routeData = new RouteData(); 11: routeData.Values.Add("controller", "home"); 12: routeData.Values.Add("action", "index"); 13: routeData.Values.Add("id", "002"); 14: RequestContext requestContext = new RequestContext(contextWrapper, routeData); 15: RouteHelper helper = new RouteHelper(requestContext); 16: 17: Response.Write(helper.Action("GetProduct", "Products",new {id="002"}) + "
"); 18: Response.Write(helper.Action("GetProduct", "Products", new { id = "002" }, "http") + "
"); 19: Response.Write(helper.Action("GetProduct", "Products", new RouteValueDictionary { { "id", "002" } }, 20: "https", "") + "
"); 21: } 22: }
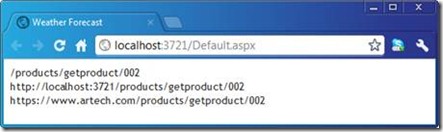
我们通过调用RouteHelper其中其中三个Action方法重载生成出三个Url并写入HTTP回复。对于第一个方法调用,我们指定了Action和Controller的名称以及针对变量{id}的值;第二次在这基础上显示指定了传输协议名称http;第三个在同时指定了协议名称(https)和主机名称()。当我们通过浏览器访问该Web页面的时候,我们会得到如下图所示3个URL。
四、UrlHelper.RouteUrl V.S. HtmlHelper.RouteLink
不论是UrlHelper的Action方法,还是HtmlHelper的ActionLink,生成的URL都是通过一个路由表生成出来的,而在默认的情况下这个路由表就是通过RouteTable的静态属性Routes表示的全局路由表,换句话说,具体使用的总是路由表中第一个匹配的路由对象。但是在有的时候,我们需要针对注册的某个具体的路由对象来生成URL或者对应的链接,这时候就需要使用的UrlHelper和HtmlHelper的另外一组方法了。
如下面的代码片断所示,UrlHelper定义了一系列的RouteUrl方法。除了第一个重载之外,后面的重载都接受一个路由对象注册名称的参数routeName。和UrlHelper的Action方法一样,我们可以通过参数指定用于替换定义在URL模板中变量的RouteValueDictionary对象(routeValues),以及传输协议和主机名称(hostName)。
1: public class UrlHelper 2: { 3: //其他成员 4: public string RouteUrl(object routeValues); 5: public string RouteUrl(string routeName); 6: public string RouteUrl(RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 7: public string RouteUrl(string routeName, object routeValues); 8: public string RouteUrl(string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 9: public string RouteUrl(string routeName, object routeValues, string protocol); 10: public string RouteUrl(string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, string protocol, string hostName); 11: }
对于没有指定路由对象注册名称的RouteUrl方法来说,它还是利用整个路由表进行URL的生成,如果显示指定了路由对象的注册名称,那么就会从路由表中获取相应的路由对象,如果该路由对象与指定的变量列表不匹配,则返回Null;否则返回生成的URL。
HtmlHelper也同样定义了类似的RouteLink方法重载用于实现基于指定路由对象的链接生成,具体的RouteLink方法定义如下。
1: public static class LinkExtensions 2: { 3: //其他成员 4: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, object routeValues); 5: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string routeName); 6: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 7: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 8: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues); 9: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, IDictionary<string, object> htmlAttributes); 10: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string routeName, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 11: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string routeName, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, IDictionary<string, object> htmlAttributes); 12: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string routeName, string protocol, string hostName, string fragment, object routeValues, object htmlAttributes); 13: public static MvcHtmlString RouteLink(this HtmlHelper htmlHelper, string linkText, string routeName, string protocol, string hostName, string fragment, RouteValueDictionary routeValues, IDictionary<string, object> htmlAttributes);