Linux设备驱动程序学习(5)-高级字符驱动程序操作[(2)阻塞型I/O和休眠]
这一部分主要讨论:
如果驱动程序无法立即满足请求,该如何响应?
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
一、休眠
进程被置为休眠,意味着它被标识为处于一个特殊的状态并且从调度器的运行队列中移走。这个进程将不被在任何 CPU 上调度,即将不会运行。 直到发生某些事情改变了那个状态。安全地进入休眠的两条规则:
(1) 永远不要在原子上下文中进入休眠,即当驱动在持有一个自旋锁、seqlock或者 RCU 锁时不能睡眠;关闭中断也不能睡眠。持有一个信号量时休眠是合法的,但你应当仔细查看代码:如果代码在持有一个信号量时睡眠,任何其他的等待这个信号量的线程也会休眠。因此发生在持有信号量时的休眠必须短暂,而且决不能阻塞那个将最终唤醒你的进程。
(2)当进程被唤醒,它并不知道休眠了多长时间以及休眠时发生什么;也不知道是否另有进程也在休眠等待同一事件,且那个进程可能在它之前醒来并获取了所等待的资源。所以不能对唤醒后的系统状态做任何的假设,并必须重新检查等待条件来确保正确的响应。
除非确信其他进程会在其他地方唤醒休眠的进程,否则也不能睡眠。使进程可被找到意味着:需要维护一个称为等待队列的
数据结构。它是一个进程链表,其中饱含了等待某个特定事件的所有进程。在 Linux 中, 一个等待队列由一个wait_queue_head_t
结构体来管理,其定义在中。wait_queue_head_t 类型的数据结构非常简单:
struct __wait_queue_head {
spinlock_t lock;
struct list_head task_list;
};
typedef struct __wait_queue_head wait_queue_head_t;
它包含一个自旋锁和一个链表。这个链表是一个等待队列入口,它被声明做 wait_queue_t。wait_queue_head_t包含关于睡眠进程的信息和它想怎样被唤醒。
简单休眠(其实是高级休眠的宏)
Linux 内核中最简单的休眠方式是称为 wait_event的宏(及其变种),它实现了休眠和进程等待的条件的检查。形式如下:
|
wait_event(queue, condition)/*不可中断休眠,不推荐*/
wait_event_interruptible(queue, condition)/*推荐,返回非零值意味着休眠被中断,且驱动应返回 -ERESTARTSYS*/
wait_event_timeout(queue, condition, timeout)
wait_event_interruptible_timeout(queue, condition, timeout)
/*有限的时间的休眠;若超时,则不管条件为何值返回0,*/
|
唤醒休眠进程的函数称为 wake_up,形式如下:
|
void wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
void wake_up_interruptible(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
|
惯例:用 wake_up 唤醒 wait_event ;用 wake_up_interruptible 唤醒wait_event_interruptible。
阻塞和非阻塞操作
全功能的 read 和 write 方法涉及到进程可以决定是进行非阻塞 I/O还是阻塞 I/O操作。明确的非阻塞 I/O 由 filp->f_flags 中的 O_NONBLOCK 标志来指示(定义再 ,被 自动包含)。浏览源码,会发现O_NONBLOCK 的另一个名字:O_NDELAY ,这是为了兼容 System V 代码。O_NONBLOCK 标志缺省地被清除,因为等待数据的进程的正常行为只是睡眠.
其实不一定只有read 和 write 方法有阻塞操作,open也可以有阻塞操作。后面会见到。而我的项目有一个和CPLD的接口的驱动,我决定要在ioctl 中使用阻塞。
高级休眠
步骤:
(1)分配和初始化一个 wait_queue_t 结构, 随后将其添加到正确的等待队列。
(2)设置进程状态,标记为休眠。在 中定义有几个任务状态:TASK_RUNNING 意思是进程能够运行。有 2 个状态指示一个进程是在睡眠: TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE 和 TASK_UNTINTERRUPTIBLE。2.6 内核的驱动代码通常不需要直接操作进程状态。但如果需要这样做使用的代码是:
|
void set_current_state(int new_state);
|
在老的代码中, 你常常见到如此的东西:current->state =
TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE; 但是象这样直接改变 current 是不推荐的,当数据结构改变时这样的代码将会失效。通过改变
current 状态,只改变了调度器对待进程的方式,但进程还未让出处理器。
(3) 最后一步是放弃处理器。 但必须先检查进入休眠的条件。如果不做检查会引入竞态: 如果在忙于上面的这个过程时有其他的线程刚刚试图唤醒你,你可能错过唤醒且长时间休眠。因此典型的代码下:
|
if (!condition)
schedule();
|
如果代码只是从 schedule 返回,则进程处于TASK_RUNNING 状态。 如果不需睡眠而跳过对 schedule 的调用,必须将任务状态重置为 TASK_RUNNING,还必要从等待队列中去除这个进程,否则它可能被多次唤醒。
手工休眠
|
/* (1)创建和初始化一个等待队列。常由宏定义完成:*/
DEFINE_WAIT(my_wait);
/*name 是等待队列入口项的名字. 也可以用2步来做:*/
wait_queue_t my_wait;
init_wait(&my_wait);
/*常用的做法是放一个 DEFINE_WAIT 在循环的顶部,来实现休眠。*/
/* (2)添加等待队列入口到队列,并设置进程状态:*/
void prepare_to_wait(wait_queue_head_t *queue, wait_queue_t *wait, int state);
/*queue 和 wait 分别地是等待队列头和进程入口。state 是进程的新状态:TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE(可中断休眠,推荐)或TASK_UNINTERRUPTIBLE(不可中断休眠,不推荐)。*/
/* (3)在检查确认仍然需要休眠之后调用 schedule*/
schedule();
/* (4)schedule 返回,就到了清理时间:*/
void finish_wait(wait_queue_head_t *queue, wait_queue_t *wait);
|
认真地看简单休眠中的 wait_event(queue, condition) 和 wait_event_interruptible(queue, condition) 底层源码会发现,其实他们只是手工休眠中的函数的组合。所以怕麻烦的话还是用wait_event比较好。
独占等待
当一个进程调用 wake_up 在等待队列上,所有的在这个队列上等待的进程被置为可运行的。
这在许多情况下是正确的做法。但有时,可能只有一个被唤醒的进程将成功获得需要的资源,而其余的将再次休眠。这时如果等待队列中的进程数目大,这可能严重
降低系统性能。为此,内核开发者增加了一个“独占等待”选项。它与一个正常的睡眠有 2 个重要的不同:
(1)当等待队列入口设置了 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSEVE 标志,它被添加到等待队列的尾部;否则,添加到头部。
(2)当 wake_up 被在一个等待队列上调用, 它在唤醒第一个有 WQ_FLAG_EXCLUSIVE 标志的进程后停止唤醒.但内核仍然每次唤醒所有的非独占等待。
采用独占等待要满足 2 个条件:
(1)希望对资源进行有效竞争;
(2)当资源可用时,唤醒一个进程就足够来完全消耗资源。
使一个进程进入独占等待,可调用:
|
void prepare_to_wait_exclusive(wait_queue_head_t *queue, wait_queue_t *wait, int state);
|
注意:无法使用 wait_event 和它的变体来进行独占等待.
唤醒的相关函数
很少会需要调用wake_up_interruptible 之外的唤醒函数,但为完整起见,这里是整个集合:
|
wake_up(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
wake_up_interruptible(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
/*wake_up
唤醒队列中的每个非独占等待进程和一个独占等待进程。wake_up_interruptible 同样,
除了它跳过处于不可中断休眠的进程。它们在返回之前, 使一个或多个进程被唤醒、被调度(如果它们被从一个原子上下文调用, 这就不会发生).*/
wake_up_nr(wait_queue_head_t *queue, int nr);
wake_up_interruptible_nr(wait_queue_head_t *queue, int nr);
/*这些函数类似 wake_up, 除了它们能够唤醒多达 nr 个独占等待者, 而不只是一个. 注意传递 0 被解释为请求所有的互斥等待者都被唤醒*/
wake_up_all(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
wake_up_interruptible_all(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
/*这种 wake_up 唤醒所有的进程, 不管它们是否进行独占等待(可中断的类型仍然跳过在做不可中断等待的进程)*/
wake_up_interruptible_sync(wait_queue_head_t *queue);
/*
一个被唤醒的进程可能抢占当前进程, 并且在 wake_up 返回之前被调度到处理器。 但是, 如果你需要不要被调度出处理器时,可以使用
wake_up_interruptible 的"同步"变体. 这个函数最常用在调用者首先要完成剩下的少量工作,且不希望被调度出处理器时。*/
|
poll 和 select
当应用程序需要进行对多文件读写时,若某个文件没有准备好,则系统会处于读写阻塞的状态,并影响了其他文件的读写。为了避免这种情况,在必须使用多
输入输出流又不想阻塞在它们任何一个上的应用程序常将非阻塞 I/O 和 poll(System V)、select(BSD Unix)、
epoll(linux2.5.45开始)系统调用配合使用。当poll函数返回时,会给出一个文件是否可读写的标志,应用程序根据不同的标志读写相应的
文件,实现非阻塞的读写。这些系统调用功能相同:
允许进程来决定它是否可读或写一个或多个文件而不阻塞。这些调用也可阻塞进程直到任何一个给定集合的文件描述符可用来读或写。这些调用都需要来自设备驱动
中poll 方法的支持,poll返回不同的标志,告诉主进程文件是否可以读写,其原型(定义在 ):
|
unsigned int (*poll) (struct file *filp, poll_table *wait);
|
实现这个设备方法分两步:
1. 在一个或多个可指示查询状态变化的等待队列上调用 poll_wait. 如果没有文件描述符可用来执行 I/O,
内核使这个进程在等待队列上等待所有的传递给系统调用的文件描述符. 驱动通过调用函数 poll_wait增加一个等待队列到 poll_table
结构,原型:
|
void poll_wait (struct file *, wait_queue_head_t *, poll_table *);
|
2. 返回一个位掩码:描述可能不必阻塞就立刻进行的操作,几个标志(通过 定义)用来指示可能的操作:
|
标志 |
含义 |
|
POLLIN |
如果设备无阻塞的读,就返回该值 |
|
POLLRDNORM |
通常的数据已经准备好,可以读了,就返回该值。通常的做法是会返回(POLLLIN|POLLRDNORA) |
|
POLLRDBAND |
如果可以从设备读出带外数据,就返回该值,它只可在linux内核的某些网络代码中使用,通常不用在设备驱动程序中 |
|
POLLPRI |
如果可以无阻塞的读取高优先级(带外)数据,就返回该值,返回该值会导致select报告文件发生异常,以为select八带外数据当作异常处理 |
|
POLLHUP |
当读设备的进程到达文件尾时,驱动程序必须返回该值,依照select的功能描述,调用select的进程被告知进程时可读的。 |
|
POLLERR |
如果设备发生错误,就返回该值。 |
|
POLLOUT |
如果设备可以无阻塞地些,就返回该值 |
|
POLLWRNORM |
设备已经准备好,可以写了,就返回该值。通常地做法是(POLLOUT|POLLNORM) |
|
POLLWRBAND |
于POLLRDBAND类似 |
考虑 poll 方法的 scullpipe 实现:
|
static unsigned int scull_p_poll(struct file *filp, poll_table *wait)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int mask = 0;
/*
* The buffer is circular; it is considered full
* if "wp" is right behind "rp" and empty if the
* two are equal.
*/
down(&dev->sem);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq, wait);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq, wait);
if (dev->rp != dev->wp)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; /* readable */
if (spacefree(dev))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; /* writable */
up(&dev->sem);
return mask;
}
|
与read 和write 的交互
正确实现poll调用的规则:
从设备读取数据:
(1)如果在输入缓冲中有数据,read 调用应当立刻返回,即便数据少于应用程序要求的,并确保其他的数据会很快到达。 如果方便,可一直返回小于请求的数据,但至少返回一个字节。在这个情况下,poll 应当返回 POLLIN|POLLRDNORM。
(2)如果在输入缓冲中无数据,read默认必须阻塞直到有一个字节。若O_NONBLOCK 被置位,read 立刻返回 -EAGIN 。在这个情况下,poll 必须报告这个设备是不可读(清零POLLIN|POLLRDNORM)的直到至少一个字节到达。
(3)若处于文件尾,不管是否阻塞,read 应当立刻返回0,且poll 应该返回POLLHUP。
向设备写数据
(1)若输出缓冲有空间,write 应立即返回。它可接受小于调用所请求的数据,但至少必须接受一个字节。在这个情况下,poll应返回 POLLOUT|POLLWRNORM。
(2)若输出缓冲是满的,write默认阻塞直到一些空间被释放。若
O_NOBLOCK 被设置,write 立刻返回一个 -EAGAIN。在这些情况下, poll
应当报告文件是不可写的(清零POLLOUT|POLLWRNORM). 若设备不能接受任何多余数据, 不管是否设置了
O_NONBLOCK,write 应返回 -ENOSPC("设备上没有空间")。
(3)永远不要让write在返回前等待数据的传输结束,即使O_NONBLOCK 被清除。若程序想保证它加入到输出缓冲中的数据被真正传送, 驱动必须提供一个 fsync 方法。
刷新待处理输出
若一些应用程序需要确保数据被发送到设备,就实现必须fsync 方法。对 fsync 的调用只在设备被完全刷新时(即输出缓冲为空)才返回,不管 O_NONBLOCK 是否被设置,即便这需要一些时间。其原型是:
|
int (*fsync) (struct file *file, struct dentry *dentry, int datasync);
|
底层数据结构
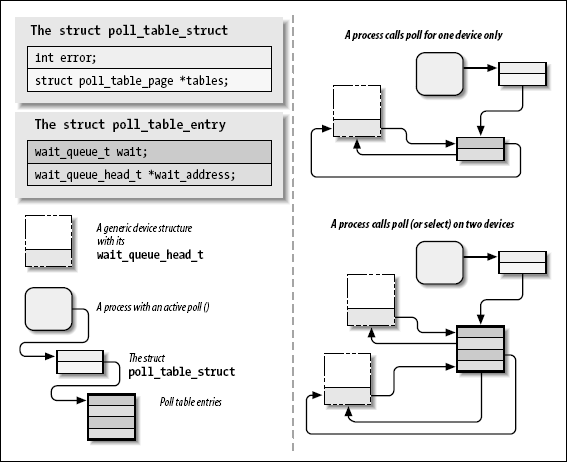
只要用户应用程序调用 poll、select、或epoll_ctl,内核就会调用这个系统调用所引用的所有文件的 poll 方法,并向他们传递同一个poll_table。 poll_table 结构只是构成实际数据结构的简单封装:
struct poll_table_struct;
/*
* structures and helpers for f_op->poll implementations
*/
typedef void (*poll_queue_proc)(struct file *, wait_queue_head_t *, struct poll_table_struct *);
typedef struct poll_table_struct {
poll_queue_proc qproc;
} poll_table;
|
对于 poll和 select系统调用,poll_table 是一个包含 poll_table_entry 结构内存页链表。
struct poll_table_entry {
struct file * filp;
wait_queue_t wait;
wait_queue_head_t * wait_address;
};
|
对 poll_wait 的调用有时还会将进程添加到给定的等待队列。整个的结构必须由内核维护,在 poll 或者 select 返回前,进程可从所有的队列中去除, .
如果被轮询的驱动没有一个驱动程序指明可进行非阻塞I/O,poll 调用会简单地睡眠,直到一个它所在的等待队列(可能许多)唤醒它.
当 poll 调用完成,poll_table 结构被重新分配, 所有的之前加入到 poll 表的等待队列入口都会从表和它们的等待队列中移出.
struct poll_wqueues {
poll_table pt;
struct poll_table_page * table;
int error;
int inline_index;
struct poll_table_entry inline_entries[N_INLINE_POLL_ENTRIES];
};
struct poll_table_page {
struct poll_table_page * next;
struct poll_table_entry * entry;
struct poll_table_entry entries[0];
};
|
异步通知
通过使用异步通知,应用程序可以在数据可用时收到一个信号,而无需不停地轮询。
启用步骤:
(1)它们指定一个进程作为文件的拥有者:使用 fcntl 系统调用发出 F_SETOWN 命令,这个拥有者进程的 ID 被保存在 filp->f_owner。目的:让内核知道信号到达时该通知哪个进程。
(2)使用 fcntl 系统调用,通过 F_SETFL 命令设置 FASYNC 标志。
内核操作过程
1.F_SETOWN被调用时filp->f_owner被赋值。
2. 当 F_SETFL 被执行来打开 FASYNC, 驱动的 fasync 方法被调用.这个标志在文件被打开时缺省地被清除。
3. 当数据到达时,所有的注册异步通知的进程都会被发送一个 SIGIO 信号。
Linux 提供的通用方法是基于一个数据结构和两个函数,定义在。
数据结构:
|
struct fasync_struct {
int magic;
int fa_fd;
struct fasync_struct *fa_next; /* singly linked list */
struct file *fa_file;
};
|
驱动调用的两个函数的原型:
|
int fasync_helper(int fd, struct file *filp, int mode, struct fasync_struct **fa);
void kill_fasync(struct fasync_struct **fa, int sig, int band);
|
当一个打开的文件的
FASYNC标志被修改时,调用fasync_helper 来从相关的进程列表中添加或去除文件。除了最后一个参数, 其他所有参数都时被提供给
fasync 方法的相同参数并被直接传递。 当数据到达时,kill_fasync 被用来通知相关的进程,它的参数是被传递的信号(常常是
SIGIO)和 band(几乎都是 POLL_IN)。
这是 scullpipe 实现 fasync 方法的:
|
static int scull_p_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int mode)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
return fasync_helper(fd, filp, mode, &dev->async_queue);
}
|
当数据到达, 下面的语句必须被执行来通知异步读者. 因为对 sucllpipe 读者的新数据通过一个发出 write 的进程被产生, 这个语句出现在 scullpipe 的 write 方法中:
if (dev->async_queue)
kill_fasync(&dev->async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN); /* 注意, 一些设备也针对设备可写而实现了异步通知,在这个情况,kill_fasnyc 必须以 POLL_OUT 模式调用.*/
|
当
文件被关闭时必须调用fasync 方法,来从活动的异步读取进程列表中删除该文件。尽管这个调用仅当 filp->f_flags 被设置为
FASYNC 时才需要,但不管什么情况,调用这个函数不会有问题,并且是普遍的实现方法。 以下是 scullpipe 的 release
方法的一部分:
/* remove this filp from the asynchronously notified filp's */
scull_p_fasync(-1, filp, 0);
|
异步通知使用的数据结构和 struct wait_queue 几乎相同,因为他们都涉及等待事件。区别异步通知用 struct file 替代 struct task_struct. 队列中的 file 用获取 f_owner, 一边给进程发送信号。
===================================================================================
驱动程序:
/*
* scullpipe.c --- fifo drive for scull
* Author: dengwei
*/
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include /* printk(), min() */
#include /* kmalloc() */
#include /* everything... */
#include
#include /* error codes */
#include /* size_t */
#include /* O_ACCMODE ,filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK*/
#include /* poll,poll_table */
#include /* creat_class() */
#include
#include /* access_ok */
#include
#include /* TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE,schedule()...*/
#include "scullpipe.h"
int scull_major = SCULL_MAJOR;
int scull_minor = 0;
int scull_p_nr_devs = SCULL_P_NR_DEVS; /* number of pipe devices */
int scull_p_buffer = SCULL_P_BUFFER; /* buffer size */ //#define SCULL_P_BUFFER 4000
static dev_t scull_p_devno; /* Our first device number */
static struct class *scull_class0;
//static struct class *scull_class1;
struct scull_pipe {
wait_queue_head_t inq, outq; /* read and write queues */
char *buffer, *end; /* begin of buf, end of buf */
int buffersize; /* used in pointer arithmetic */
char *rp, *wp; /* where to read, where to write */
int nreaders, nwriters; /* number of openings for r/w */
struct fasync_struct *async_queue; /* asynchronous readers */
struct semaphore sem; /* mutual exclusion semaphore */
struct cdev cdev; /* Char device structure */
};
static struct scull_pipe *scull_p_devices;
static int scull_p_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int mode);
static int spacefree(struct scull_pipe *dev);
/*
* Open and close
*/
static int scull_p_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev;
dev = container_of(inode->i_cdev, struct scull_pipe, cdev); // 注册一个自己的结构体
filp->private_data = dev;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS; // 加锁
//生成缓冲区间
if (!dev->buffer) {
/* allocate the buffer */
dev->buffer = kmalloc(scull_p_buffer, GFP_KERNEL);
if (!dev->buffer) {
up(&dev->sem);
return -ENOMEM;
}
}
dev->buffersize = scull_p_buffer; //#define SCULL_P_BUFFER 4000
dev->end = dev->buffer + dev->buffersize;
dev->rp = dev->wp = dev->buffer; /* rd and wr from the beginning */
/* use f_mode,not f_flags: it's cleaner (fs/open.c tells why) */
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_READ) /* 文件的打开模式*/
dev->nreaders++;
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE)
dev->nwriters++; // 根据进程对文件的读写要求,分别记录进程读写打开设备的次数dev->nreaders,dev->nwriters
/*f_mode表示进程的读写等模式,f_flag表示文件本身的一些设定*/
up(&dev->sem); // 解锁
return nonseekable_open(inode, filp); // 通知内核不支持 llseek
}
static int scull_p_close(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
/* remove this filp from the asynchronously notified filp's */
scull_p_fasync(-1, filp, 0); // 关闭本设备的异步通知:scull_p_fasync(-1, filp, 0);
down(&dev->sem);
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_READ)
dev->nreaders--;
if (filp->f_mode & FMODE_WRITE)
dev->nwriters--; // 记录读写的次数
if (dev->nreaders + dev->nwriters == 0) {
kfree(dev->buffer);
dev->buffer = NULL; /* the other fields are not checked on open */
}
/*
//在互斥锁的保护下处理打开进程记录和环形缓冲
//dev->nreaders,dev->nwriters分别递减
//如果两者和为0,即无进程打开设备,则清空设备的环形缓冲
*/
up(&dev->sem);
return 0;
}
/*
* Data management: read and write
*/
/*阻塞读;若无可读数据进入休眠;使用环形缓冲;最后还唤醒休眠中的写进程*/
static ssize_t scull_p_read (struct file *filp, char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data; //dev 和文件连接 //通过filp->private_data获得设备结构体的入口指针
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem)) //加锁down_interruptible(&dev->sem)
return -ERESTARTSYS;
while (dev->rp == dev->wp) { /* nothing to read */ //若缓冲区为空,则进入以下循环,以实现阻塞读等待
//解锁up (&dev->sem)/*由于阻塞等待有数据写入,首先要解锁数据区*/
up(&dev->sem); /* release the lock */
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN; //不完整的非阻塞操作
PDEBUG("\"%s\" reading: going to sleep\n", current->comm);
if (wait_event_interruptible(dev->inq, (dev->rp != dev->wp))) //进入睡眠等待在写函数中的唤醒
return -ERESTARTSYS; /* signal: tell the fs layer to handle it*/ //若等待函数非正常唤醒则返回值为非0,这时候应该返回-ERESTARTSYS,
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem)) /* otherwise loop, but first reacquire the lock */
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
/* ok, data is there, return something */
/* 通过rp,wp的关系计算实际能读取的数据长度,注意环形缓冲wp反转后的处理,即返回rp到指针结束的数 */
if (dev->wp > dev->rp)
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->wp - dev->rp));
else /* the write pointer has wrapped, return data up to dev->end */
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->end - dev->rp));
if (copy_to_user(buf, dev->rp, count)) {
up (&dev->sem);
return -EFAULT;
}
dev->rp += count;
if (dev->rp == dev->end)
dev->rp = dev->buffer; /* wrapped */
up (&dev->sem);
/* finally, awake any writers and return */ //唤醒处于睡眠中写进程
wake_up_interruptible(&dev->outq);
PDEBUG("\"%s\" did read %li bytes\n",current->comm, (long)count);
return count;
}
int scull_p_ioctl(struct inode *inode, struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg)
{
int err = 0;
/*
* extract the type and number bitfields, and don't decode
* wrong cmds: return ENOTTY (inappropriate ioctl) before access_ok()
*/
if (_IOC_TYPE(cmd) != SCULL_IOC_MAGIC) return -ENOTTY;
if (_IOC_NR(cmd) > SCULL_IOC_MAXNR) return -ENOTTY; //#define SCULL_IOC_MAXNR 1
/*
* the direction is a bitmask, and VERIFY_WRITE catches R/W
* transfers. `Type' is user-oriented, while
* access_ok is kernel-oriented, so the concept of "read" and
* "write" is reversed
*/
if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_READ) //_IOC_DIR : 获取读写属性域值 (bit30 ~ bit31)
err = !access_ok(VERIFY_WRITE, (void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd)); //_IOC_SIZE : 读取数据大小域值 (bit16 ~ bit29)
else if (_IOC_DIR(cmd) & _IOC_WRITE)
err = !access_ok(VERIFY_READ, (void __user *)arg, _IOC_SIZE(cmd));
if (err) return -EFAULT;
/*
* 调用access_ok后,驱动程序可以安全的进行实际的数据传送了。
*/
//传递设备的参数配置及“unsigned long arg”的各种情况
switch(cmd) {
/*
* The following two change the buffer size for scullpipe.
* The scullpipe device uses this same ioctl method, just to
* write less code. Actually, it's the same driver, isn't it?
*/
case SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE:
scull_p_buffer = arg;
break;
case SCULL_P_IOCQSIZE:
return scull_p_buffer;
default: /* redundant, as cmd was checked against MAXNR */
return -ENOTTY;
}
return 0;
}
/* Wait for space for writing; caller must hold device semaphore. On
* error the semaphore will be released before returning. */
static int scull_getwritespace(struct scull_pipe *dev, struct file *filp)
{
while (spacefree(dev) == 0) { /* full */
DEFINE_WAIT(wait);
up(&dev->sem);
if (filp->f_flags & O_NONBLOCK)
return -EAGAIN;
PDEBUG("\"%s\" writing: going to sleep\n",current->comm);
prepare_to_wait(&dev->outq, &wait, TASK_INTERRUPTIBLE);
if (spacefree(dev) == 0) //在放入队列前检查缓冲区
schedule(); //进入休眠 schedule()的用法查看http://blog.chinaunix.net/u2/89923/showart_1772861.html
finish_wait(&dev->outq, &wait); //schedule()之后的清理
if (signal_pending(current))
return -ERESTARTSYS; /* signal: tell the fs layer to handle it */
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
}
return 0;
}
/* How much space is free? */
//判断有多少空间可用,调用:spacefree(dev),注意其中可写空间为空空间-1
static int spacefree(struct scull_pipe *dev)
{
if (dev->rp == dev->wp)
return dev->buffersize - 1;
return ((dev->rp + dev->buffersize - dev->wp) % dev->buffersize) - 1; //计算可写空间-1
}
static ssize_t scull_p_write(struct file *filp, const char __user *buf, size_t count, loff_t *f_pos)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data; //通过filp->private_data获得设备结构体的入口指针
int result;
if (down_interruptible(&dev->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
/* Make sure there's space to write */
result = scull_getwritespace(dev, filp); //现了手动休眠以阻塞等待可写
if (result)
return result; /* scull_getwritespace called up(&dev->sem) */
//使用手动休眠的方式等待有空间可写,其实就是等待读进程返回
/* ok, space is there, accept something */
//再通过rp,wp计算实际本次可写数据的长度
count = min(count, (size_t)spacefree(dev));
if (dev->wp >= dev->rp)
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->end - dev->wp)); /* to end-of-buf */
else /* the write pointer has wrapped, fill up to rp-1 */
count = min(count, (size_t)(dev->rp - dev->wp - 1));
PDEBUG("Going to accept %li bytes to %p from %p\n", (long)count, dev->wp, buf);
if (copy_from_user(dev->wp, buf, count)) {
up (&dev->sem);
return -EFAULT;
}
dev->wp += count;
if (dev->wp == dev->end)
dev->wp = dev->buffer; /* wrapped */
up(&dev->sem);
/* finally, awake any reader */
wake_up_interruptible(&dev->inq); /* blocked in read() and select() */
/* and signal asynchronous readers, explained late in chapter 5 */
// 非同步通知:http://dev.firnow.com/course/6_system/linux/Linuxjs/2008930/147083_2.html
// 当数据来到时候,通知异步读取
if (dev->async_queue)
kill_fasync(&dev->async_queue, SIGIO, POLL_IN);
PDEBUG("\"%s\" did write %li bytes\n",current->comm, (long)count);
return count;
}
/*用户空间poll/select方法驱动里面的实现*/
static unsigned int scull_p_poll(struct file *filp, poll_table *wait)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
unsigned int mask = 0;
/*
* The buffer is circular; it is considered full
* if "wp" is right behind "rp" and empty if the
* two are equal.
*/
down(&dev->sem);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq, wait);
poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq, wait);//将读写等待队列进入休眠:poll_wait(filp, &dev->inq,wait) & poll_wait(filp, &dev->outq,wait);
if (dev->rp != dev->wp)
mask |= POLLIN | POLLRDNORM; /* readable */
if (spacefree(dev))
mask |= POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM; /* writable */
up(&dev->sem); // 唤醒后通过环形缓冲的wp,rp判断可读可写
return mask; // 可读返回:POLLIN | POLLRDNORM 可写:POLLOUT | POLLWRNORM
}
//关闭本设备的异步通知:scull_p_fasync(-1, filp, 0);
static int scull_p_fasync(int fd, struct file *filp, int mode)
{
struct scull_pipe *dev = filp->private_data;
return fasync_helper(fd, filp, mode, &dev->async_queue);
}
/* FIXME this should use seq_file */
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
static void scullp_proc_offset(char *buf, char **start, off_t *offset, int *len)
{
if (*offset == 0)
return;
if (*offset >= *len) { /* Not there yet */
*offset -= *len;
*len = 0;
}
else { /* We're into the interesting stuff now */
*start = buf + *offset;
*offset = 0;
}
}
static int scull_read_p_mem(char *buf, char **start, off_t offset, int count,
int *eof, void *data)
{
int i, len;
struct scull_pipe *p;
//Linux主要采用分页机制来实现虚拟内存管理。内存页的大小为PAGE_SIZE字节
#define LIMIT (PAGE_SIZE-200) /* don't print any more after this size */
*start = buf;
len = sprintf(buf, "Default buffersize is %i\n", scull_p_buffer);
// len = buf = scull_p_buffer
for(i = 0; i p = &scull_p_devices[i];
if (down_interruptible(&p->sem))
return -ERESTARTSYS;
len += sprintf(buf+len, "\nDevice %i: %p\n", i, p);
len += sprintf(buf+len, " Queues: %p %p\n", p->inq, p->outq);
len += sprintf(buf+len, " Buffer: %p to %p (%i bytes)\n", p->buffer, p->end, p->buffersize);
len += sprintf(buf+len, " rp %p wp %p\n", p->rp, p->wp);
len += sprintf(buf+len, " readers %i writers %i\n", p->nreaders, p->nwriters); // len == ?
up(&p->sem);
scullp_proc_offset(buf, start, &offset, &len);
}
*eof = (len <= LIMIT);
return len;
}
#endif
/*
* The file operations for the pipe device
* (some are overlayed with bare scull)
*/
struct file_operations scull_pipe_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.llseek = no_llseek,
.read = scull_p_read,
.write = scull_p_write,
.poll = scull_p_poll,
.ioctl = scull_p_ioctl,
.open = scull_p_open,
.release = scull_p_close,
.fasync = scull_p_fasync,
};
/*
* Set up a cdev entry.
*/
static void scull_p_setup_cdev(struct scull_pipe *dev, int index)
{
int err, devno = scull_p_devno + index;
cdev_init(&dev->cdev, &scull_pipe_fops);
dev->cdev.owner = THIS_MODULE;
err = cdev_add (&dev->cdev, devno, 1);
/* Fail gracefully if need be */
if (err)
printk(KERN_NOTICE "Error %d adding scullpipe%d", err, index);
}
/*
* Initialize the pipe devs; return how many we did.
*/
int scull_p_init(void)
{
int result, i;
/*
* Get a range of minor numbers to work with, asking for a dynamic
* major unless directed otherwise at load time.
*/
if (scull_major) {
scull_p_devno = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor);
result = register_chrdev_region(scull_p_devno, scull_p_nr_devs, "pipe");
} else {
result = alloc_chrdev_region(&scull_p_devno, scull_minor, scull_p_nr_devs,"pipe");
scull_major = MAJOR(scull_p_devno);
scull_p_devno = MKDEV(scull_major, scull_minor);
}
if (result < 0) {
printk(KERN_WARNING "pipe: can't get major %d\n", scull_major);
return result;
}
scull_p_devices = kmalloc(scull_p_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_pipe), GFP_KERNEL);
if (scull_p_devices == NULL) {
unregister_chrdev_region(scull_p_devno, scull_p_nr_devs);
return 0;
}
memset(scull_p_devices, 0, scull_p_nr_devs * sizeof(struct scull_pipe));
for (i = 0; i < scull_p_nr_devs; i++) {
init_waitqueue_head(&(scull_p_devices[i].inq));
init_waitqueue_head(&(scull_p_devices[i].outq));
init_MUTEX(&scull_p_devices[i].sem);
scull_p_setup_cdev(scull_p_devices + i, i);
}
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
create_proc_read_entry("scullpipe", 0, NULL, scull_read_p_mem, NULL); // 在/proc下创建scullpipe文件
#endif
/*注册一个类,使得mdev能在/dev下创建设备节点??????*/
scull_class0 = class_create(THIS_MODULE,"scullpipe0");
scull_class0 = class_create(THIS_MODULE,"scullpipe1");
if(IS_ERR(scull_class0))
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "Err:faile in scull_class!\n");
return -1;
}
/*******************************************************************
scull_class0 = class_create(THIS_MODULE,"scullpipe0");
scull_class1 = class_create(THIS_MODULE,"scullpipe1");
if(IS_ERR(scull_class0 && scull_class1))
{
printk(KERN_ALERT "Err:faile in scull_class!\n");
return -1;
}
********************************************************************/
/*创建设备节点,名字为DEVICE_NAME ,主设备号用上面动态生成的dev*/
device_create(scull_class0, NULL, scull_p_devno, NULL, "scullpipe0");
device_create(scull_class0, NULL, scull_p_devno, NULL, "scullpipe1");
printk("scullpipe0&&scullpipe1 initializa\n");
return scull_p_nr_devs;
}
/*
* This is called by cleanup_module or on failure.
* It is required to never fail, even if nothing was initialized first
*/
void scull_p_cleanup(void)
{
int i;
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
remove_proc_entry("scullpipe", NULL); // todo
#endif
if (!scull_p_devices)
return; /* nothing else to release */
for (i = 0; i < scull_p_nr_devs; i++) {
cdev_del(&scull_p_devices[i].cdev);
kfree(scull_p_devices[i].buffer);
}
kfree(scull_p_devices);
unregister_chrdev_region(scull_p_devno, scull_p_nr_devs);
scull_p_devices = NULL; /* pedantic */
device_destroy(scull_class0, scull_p_devno);
//device_destroy(scull_class1, scull_p_devno);
class_destroy(scull_class0);
//class_destroy(scull_class1);
}
module_init(scull_p_init);
module_exit(scull_p_cleanup);
MODULE_AUTHOR("Dengwei");
MODULE_LICENSE("Dual BSD/GPL");
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
头文件:
#ifndef _SCULL_H_
#define _SCULL_H_
#include /* needed for the _IOW etc stuff used later */
/*
* Macros to help debugging
*/
#undef PDEBUG /* undef it, just in case */
#ifdef SCULL_DEBUG
# ifdef __KERNEL__
/* This one if debugging is on, and kernel space */
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) printk( KERN_DEBUG "scull: " fmt, ## args)
# else
/* This one for user space */
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) fprintf(stderr, fmt, ## args)
# endif
#else
# define PDEBUG(fmt, args...) /* not debugging: nothing */
#endif
#undef PDEBUGG
#define PDEBUGG(fmt, args...) /* nothing: it's a placeholder */
#ifndef SCULL_MAJOR
#define SCULL_MAJOR 0 /* dynamic major by default */
#endif
#ifndef SCULL_P_NR_DEVS
#define SCULL_P_NR_DEVS 4 /* scullpipe0 through scullpipe3 */
#endif
/*
* The pipe device is a simple circular buffer. Here its default size
*/
#ifndef SCULL_P_BUFFER
#define SCULL_P_BUFFER 4000
#endif
/*
* Representation of scull quantum sets.
*/
/*
* Split minors in two parts
*/
#define TYPE(minor) (((minor) >> 4) & 0xf) /* high nibble */
#define NUM(minor) ((minor) & 0xf) /* low nibble */
/*
* The different configurable parameters
*/
extern int scull_major; /* main.c */
extern int scull_p_nr_devs;
extern int scull_p_buffer; /* pipe.c */
/*
* Prototypes for shared functions
*/
int scull_p_init(void);
void scull_p_cleanup(void);
/*
* Ioctl definitions
*/
/* Use 'k' as magic number */
#define SCULL_IOC_MAGIC 'k'
/* Please use a different 8-bit number in your code */
#define SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 0)
#define SCULL_P_IOCQSIZE _IO(SCULL_IOC_MAGIC, 1)
/* ... more to come */
#define SCULL_IOC_MAXNR 1
#endif /* _SCULL_H_ */
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------测试文件:
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include
#include "scull.h"
int main()
{
char buffer1[20]={0};
int pipetest0, pipetest1;
int code=21, i=0;
struct pollfd poll_list[2];
int retval;
if ((pipetest0 = open("/dev/scullpipe0",O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
printf("open scullpipe0 error! \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("open scullpipe0 ! \n");
if ((pipetest1 = open("/dev/scullpipe1",O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
printf("open scullpipe1 error! \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("open scullpipe1 ! \n");
if ( ioctl(pipetest0 , SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE , code ) < 0) {
printf("pipetest0 ioctl SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE error! \n");
exit(1);
}
printf(" SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE : scull_p_buffer0=%d !\n" ,ioctl( pipetest0 , SCULL_P_IOCQSIZE , NULL ) );
if ( ioctl(pipetest1 , SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE , code ) < 0) {
printf("pipetest1 ioctl SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE error! \n");
exit(1);
}
printf(" SCULL_P_IOCTSIZE : scull_p_buffer1=%d !\n" ,ioctl( pipetest1 , SCULL_P_IOCQSIZE , NULL ) );
close(pipetest0);
printf("close pipetest0 ! \n");
close(pipetest1);
printf("close pipetest1 ! \n");
if ((pipetest0 = open("/dev/scullpipe0",O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
printf("reopen scullpipe0 error! \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("reopen scullpipe0 ! \n");
if ((pipetest1 = open("/dev/scullpipe1",O_RDONLY)) < 0) {
printf("reopen scullpipe1 error! \n");
exit(1);
}
printf("reopen scullpipe1 ! \n");
poll_list[0].fd = pipetest0;
poll_list[1].fd = pipetest1;
poll_list[0].events = POLLIN|POLLRDNORM;
poll_list[1].events = POLLIN|POLLRDNORM;
while(1)
{
retval = poll(poll_list,(unsigned long)2,-1);
/* retval 总是大于0或为-1,因为我们在阻塞中工作 */
if(retval < 0)
{
fprintf(stderr,"poll错误: %s\n",strerror(errno));
return -1;
}
if(poll_list[0].revents&(POLLIN|POLLRDNORM))
{
if ((code=read(pipetest0 , buffer1 , 20)) != 20) printf("read from pipetest0 error! code=%d\n",code);
else printf("read from pipetest0 ok! code=%d \n",code);
for(i=0;i<20;i+=5)
printf("[%d]=%c [%d]=%c [%d]=%c [%d]=%c [%d]=%c\n",i,buffer1[i],i+1,buffer1[i+1],i+2,buffer1[i+2],i+3,buffer1[i+3],i+4,buffer1[i+4]);
}
if(poll_list[1].revents&(POLLIN|POLLRDNORM))
{
if ((code=read(pipetest1 , buffer1 , 20)) != 20) printf("read from pipetest1 error! code=%d \n",code);
else printf("read from pipetest1 ok! code=%d \n",code);
for(i=0;i<20;i+=5)
printf("[%d]=%c [%d]=%c [%d]=%c [%d]=%c [%d]=%c\n",i,buffer1[i],i+1,buffer1[i+1],i+2,buffer1[i+2],i+3,buffer1[i+3],i+4,buffer1[i+4]);
}
}
close(pipetest0 );
printf("close pipetest0 ! \n");
close(pipetest1 );
printf("close pipetest1 ! \n");
printf("\n");
exit(0);
}
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
测试结果:
root@dw:/home/dengwei/ldd3_dw/scullpipe-dw/scullpipe-test# ./pipe_test &
[1] 3857
root@dw:/home/dengwei/ldd3_dw/scullpipe-dw/scullpipe-test# open scullpipe0 !
open scullpipe1 error!
^C
[1]+ Exit 1 ./pipe_test
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
结构分析:在/dev下只生成了scullpipe0
原因:
==================================================================================
