VMware Workstation (and presumably the other enterprise-grade products in the VMware family) come with the handy “shared folders” feature which makes sharing files between a host and a virtual appliance nice and simple. The free products (VMware Player and Server) do not, unfortunately, have this ability and so we must find another way.
This quick guide shows how to use to achieve the same aim. It is aimed at Ubuntu users but (the general concepts at least) should work on any modern Linux distribution. It is also written with a Windows XP guest in mind but a similar process should work in Windows Vista, Windows 2000 and other operating systems.
The goal is to set up a network share which both operating systems can transparently read and write to.
For reference, I am using Ubuntu 7.04 (Feisty).
Which VMware?
I’ll presume you have VMWare already installed with a Windows XP guest virtual appliance already set up. This guide is aimed at users of VMware Player and Server editions (I am using VMware Player).
VMware Player is a simple:
sudo apt-get install vmware-player
away. For the Server edition, you’ll probably want to .
Install Samba
If you don’t already have Samba installed, now would be a good time to do it:
sudo apt-get install samba
In order to keeps things clean and easy to manage, we’ll set up a new user account to own the share. This account name will be used when connecting to the share from within Windows. For the purposes of illustration, I will be creating a share called sandbox with the username and group also being sandbox.
Create the new group and user account with no login privileges:
sudo groupadd sandbox
sudo useradd --gid sandbox --shell /bin/false sandbox
To avoid creating a redundant home directory, you can add:
--home /nonexistent
to the end of the previous command.
Now you need to add a matching Samba account. You’ll be prompted to set a password - make note of this as this is what you will use to connect to the share from within Windows.
sudo smbpasswd -a sandbox
Next you’ll need to create a directory to be used as the share (assuming you don’t already have one). Create a directory, setting the username to your usual login and group to sandbox. Then chmod the directory 775 (assuming you wish both yourself and the virtual appliance to have read/write access). Here is what I entered:
cd $HOME
mkdir sandbox
sudo chown russ:sandbox sandbox
sudo chmod 775 sandbox
When you write to the share from within Ubuntu, new files will be created with the default permissions 644 with the username and group being your own user account. When your Windows client connects to the share, it will access it as if it were the local system user sandbox and so the group permissions will apply and you won’t be able to write to any files created from within Ubuntu.
To get around this problem, we can set the groupid bit for the sandbox directory which means all new files created will inherit the permissions of the parent and so the sandbox user from within Windows will be able to make read and write changes as desired.
sudo chmod g+s sandbox
If you don’t understand the above, don’t worry, just chmod the directory with the command above and all should be well.
Setting up the Samba share
Now all that’s left to do is to tell Samba about our share. Open up /etc/samba/smb.conf in your favourite text editor.
sudo gedit /etc/samba/smb.conf
Firstly, we need to set the security mechanism to user. Look for the line:
security = user
and make sure it is uncommented (remove the preceding semicolon if there is one).
Now, scroll down to the Share Definitions section and add the following:
[sandbox]
path = /home/russ/sandbox
valid users = sandbox
read only = No
create mask = 0777
directory mask = 0777
Be sure to set the correct path to your share. Save the file and restart the Samba daemon:
sudo /etc/init.d/samba restart
That should be it. You should now be able to connect to your share from within the Windows guest. At this point you need to know what IP address to connect to from within Windows. This depends on what networking mode you are using for your virtual appliance.
Bridged Networking
In this mode, your guest OS has its own IP address and so the address it needs to connect to is your usual host machine’s address. In this case your address is probably the top line from the output of this command:
ifconfig | grep "inet addr:"
NAT networking
In this mode, your guest OS shares your host’s address (in terms of other machines on the LAN) and communicates with the host via a private network. In this case, the IP address you need to connect to is most likely the bottom one from the output of this command:
ifconfig | grep "inet addr:"
Connecting to the share from within Windows
If you are unsure as to your host’s IP address, try and ping it first from within the Windows guest to confirm you have the right one.
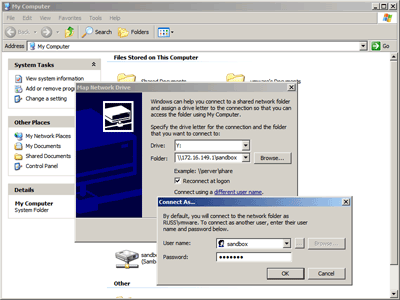
Having worked out what IP address to connect to, you should now be able to connect to your share from within Windows.
The easiest way to do this is:
- Open up My Computer
- Go to the Tools menu and then Map Network Drive
- Choose a drive letter to map the network share to
- In Folder, enter: \\HOSTIP\sandbox (replacing HOSTIP)
- Click “Connect using a different user name” and enter:
- username: sandbox
- password: yourpassword
- Click OK and then the Finish button to connect
Hopefully, congratulations are in order. If not, be sure to make sure that any firewalls you have running (host or guest) have the correct rules set to allow communication between the two systems.
A note on security
At this point, assuming you have a successful connection, it is worth noting that any other machine on your local network (and potentially the internet if you are not behind a NAT or firewall) can connect to your share (assuming they have the correct credentials).
If you are only using Samba for sharing with VMware (as I am), you may wish to restrict access to VMware only. This is quite easy to do since VMware creates virtual network interfaces for communication between hosts and guests. This means we can set Samba up to ignore any communications that do not originate from these interfaces.
To do this, open up your Samba configuration file again:
sudo gedit /etc/samba/smb.conf
Make sure you have a:
bind interfaces only = true
line and that it is uncommented (remove any preceding semicolons). Just above this should be an interfaces line (most likely commented out). Add the following just below this:
interfaces = vmnet0 vmnet1 vmnet8
These are the virtual interfaces VMware uses for each type of virtual networking: bridged, host only and NAT respectively.
After making the changes, you will need to restart Samba again:
sudo /etc/init.d/samba restart
and possibly shutdown your VMware session and restart the VMware service:
VMware Player:
sudo /etc/init.d/vmware-player restart
VMware Server:
sudo /etc/init.d/vmware restart
Finished
You should now have a Samba share configured which is only accessible from your VMware guest appliances. Good luck!
