一、Dubbo分层整体设计概述
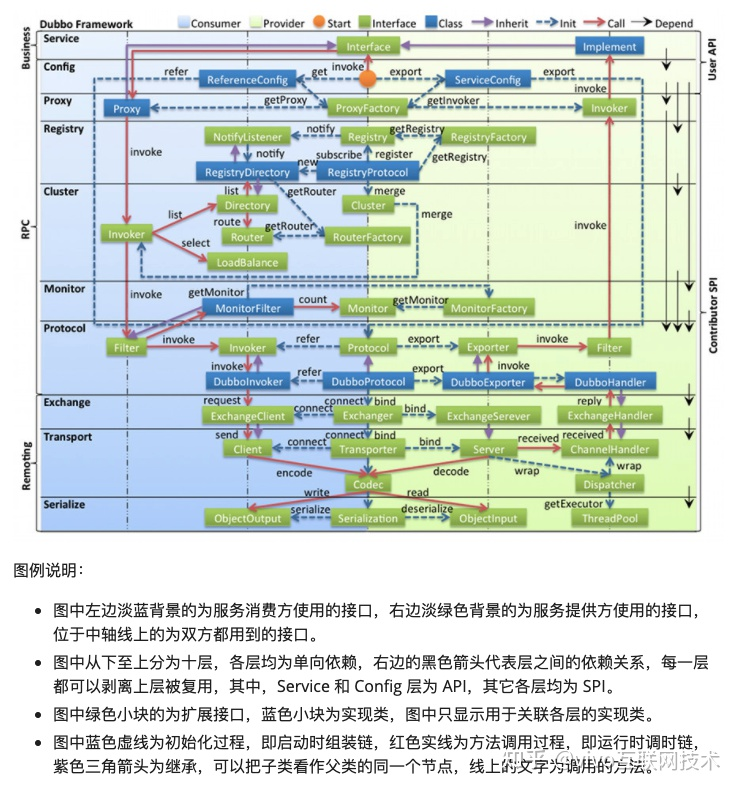
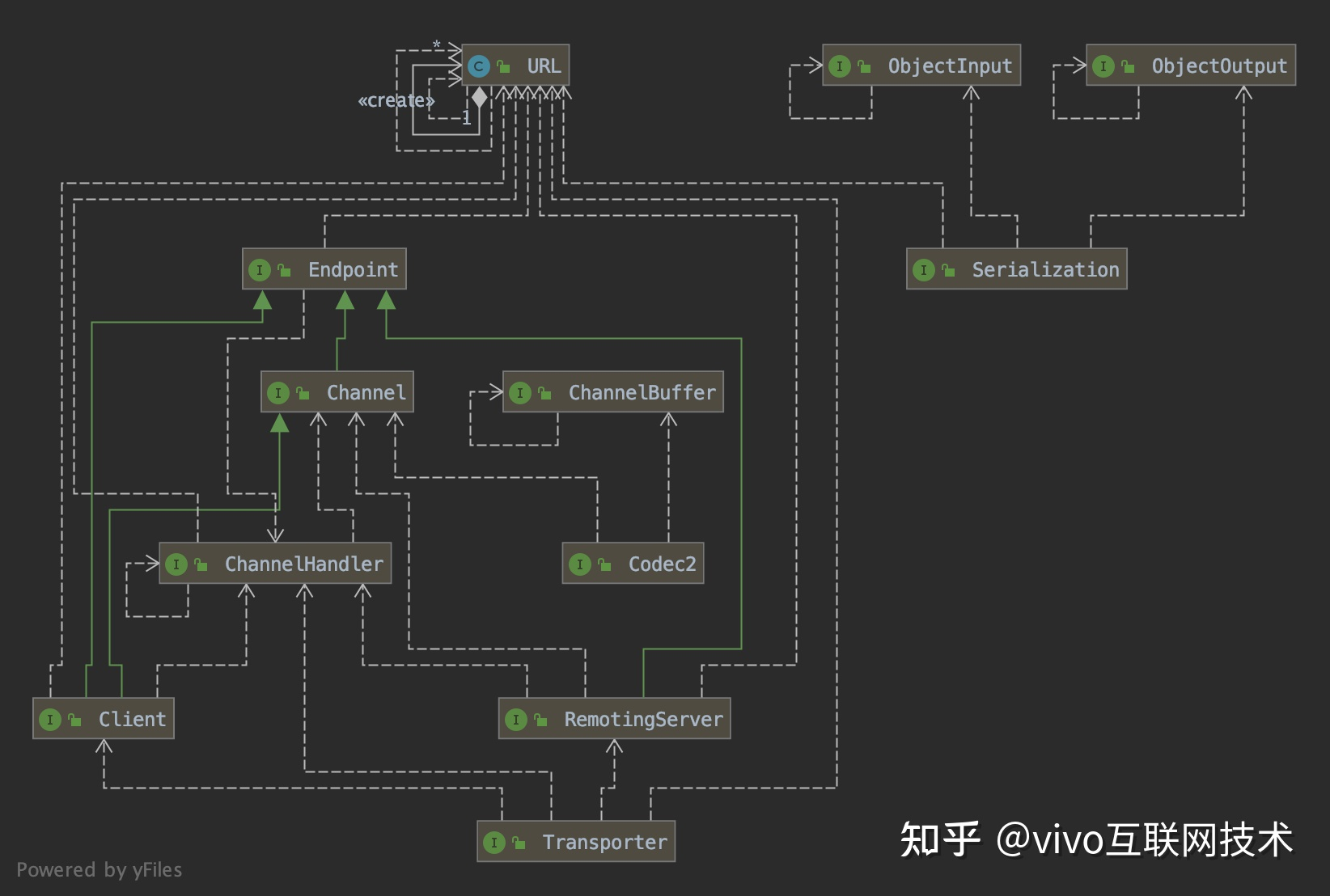
如图描述Dubbo实现的RPC整体分10层:service、config、proxy、registry、cluster、monitor、protocol、exchange、transport、serialize。
service:使用方定义的接口和实现类;
config:负责解析Dubbo定义的配置,比如注解和xml配置,各种参数;
proxy:主要负责生成消费者和提供者的代理对象,加载框架功能,比如提供者过滤器链,扩展点;
registry:负责注册服务的定义和实现类的装载;
cluster:只有消费者有这么一层,负责包装多个服务提供者成一个‘大提供者’,加载负载均衡、路有等扩展点;
monitor:定义监控服务,加载监控实现提供者;
protocol:封装RPC调用接口,管理调用实体的生命周期;
exchange:封装请求响应模式,同步转异步;
transport:抽象传输层模型,兼容netty、mina、grizzly等通讯框架;
serialize:抽象序列化模型,兼容多种序列化框架,包括:fastjson、fst、hessian2、kryo、kryo2、protobuf等,通过序列化支持跨语言的方式,支持跨语言的rpc调用;
Dubbo这么分层的目的在于实现层与层之间的解耦,每一层都定义了接口规范,也可以根据不同的业务需求定制、加载不同的实现,具有极高的扩展性。
1.1. RPC调用过程
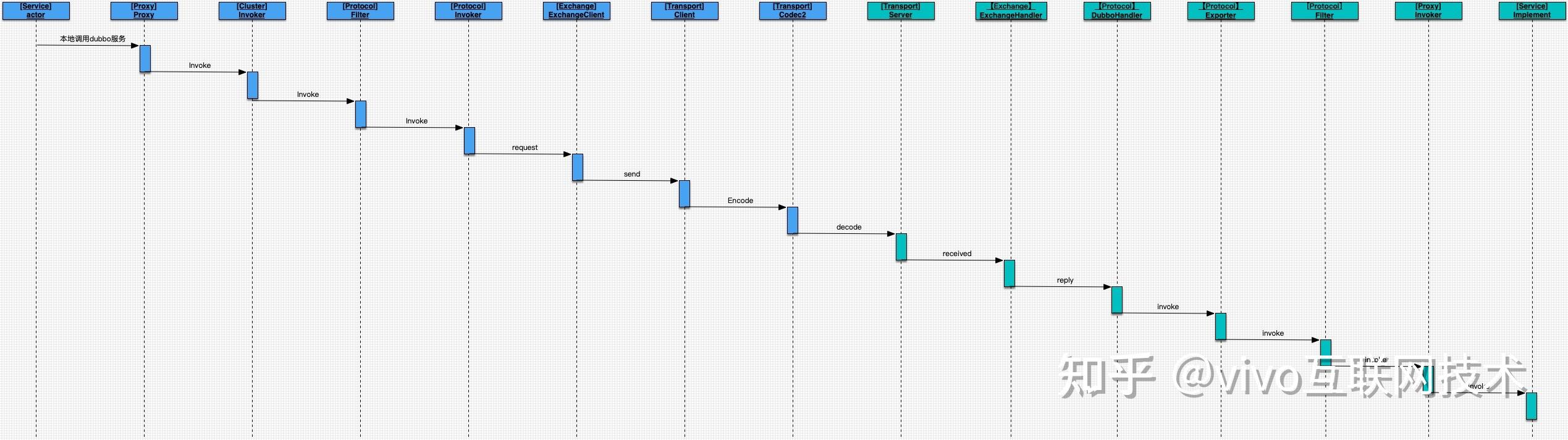
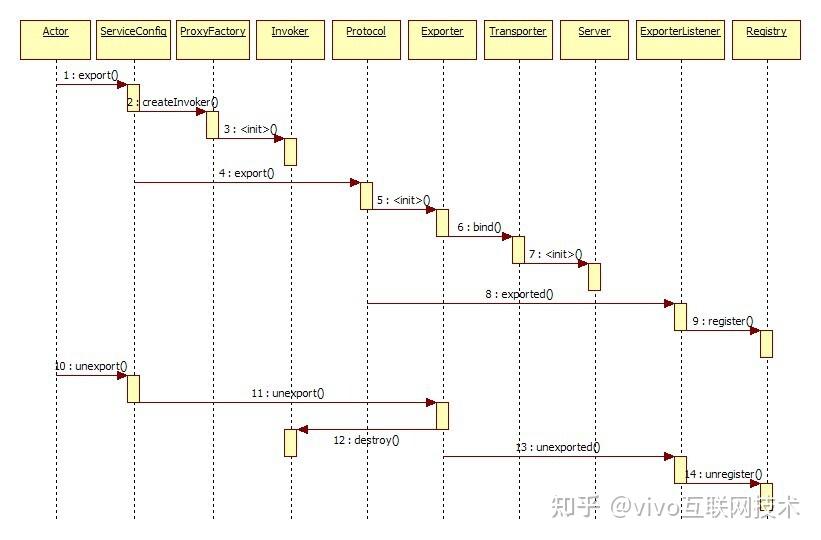
从Dubbo分层的角度看,详细时序图如下,蓝色部分是服务消费端,浅绿色部分是服务提供端,时序图从消费端一次Dubbo方法调用开始,到服务端本地方法执行结束。
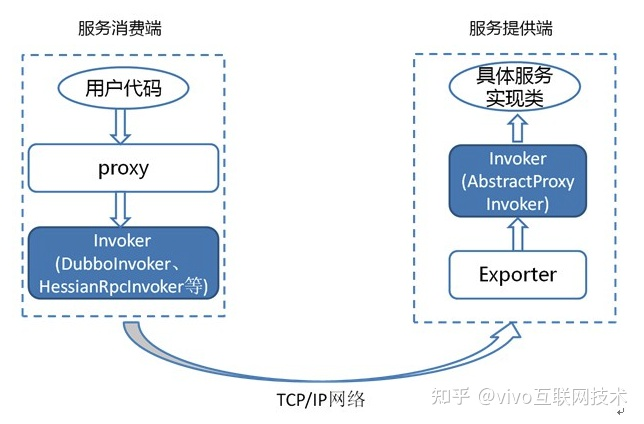
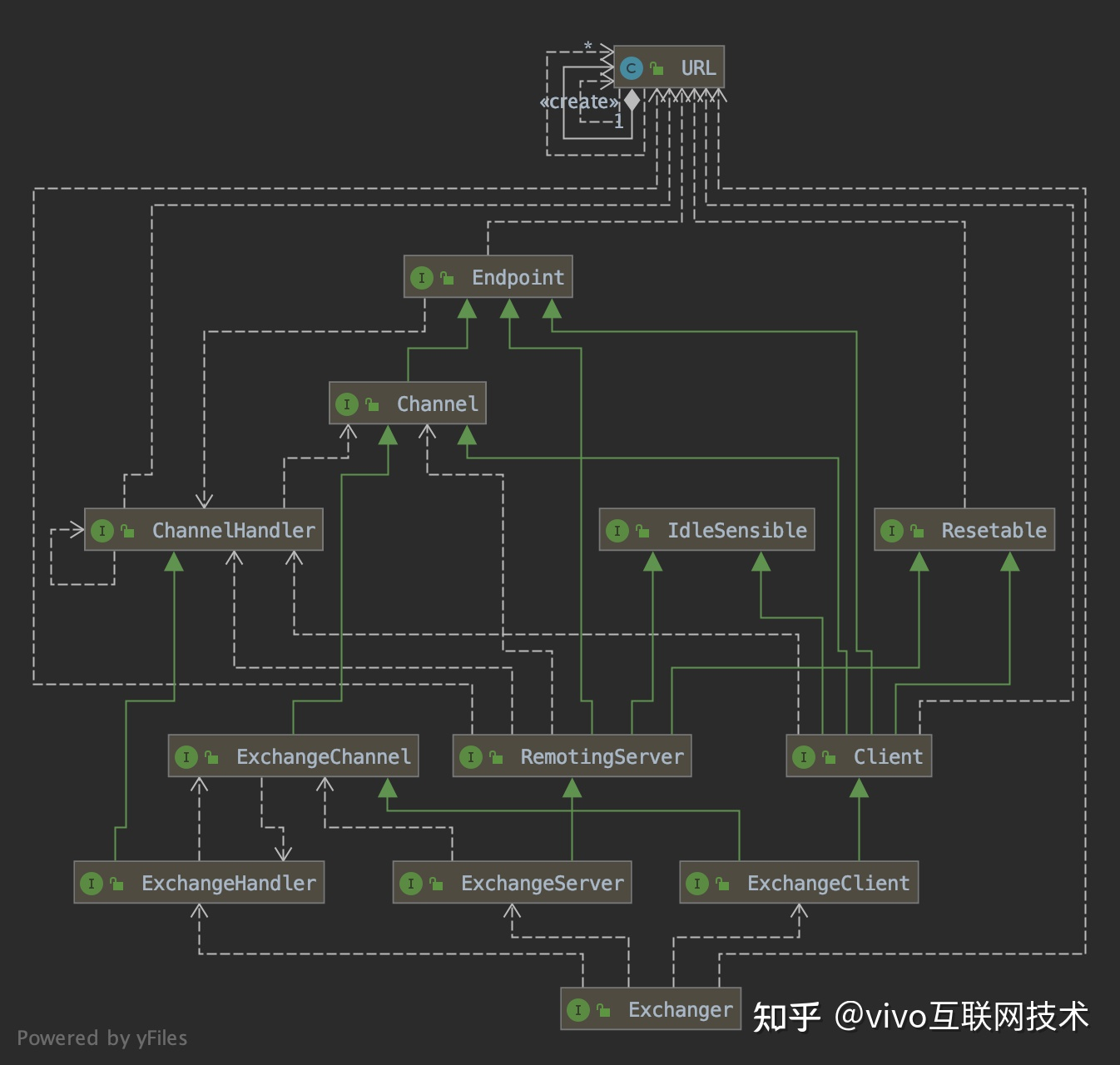
从Dubbo核心领域对象的角度看,我们引用Dubbo官方文档说明,如下图所示。Dubbo核心领域对象是Invoker,消费端代理对象是proxy,包装了Invoker的调用;服务端代理对象是一个Invoker,他通过exporter包装,当服务端接收到调用请求后,通过exporter找到Invoker,Invoker去实际执行用户的业务逻辑。
1.2 Dubbo服务的注册和发现流程
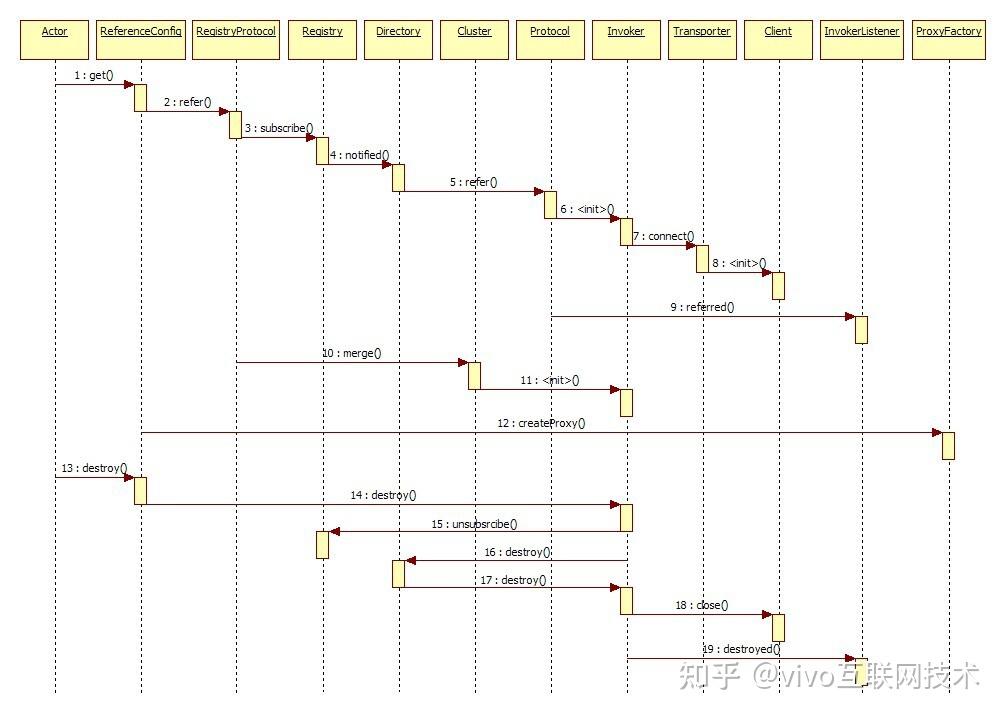
下图出自开发指南-框架设计-引用服务时序,主要流程是:从注册中心订阅服务提供者,然后启动tcp服务连接远端提供者,将多个服务提供者合并成一个Invoker,用这个Invoker创建代理对象。
接下来我们结合Dubbo服务的注册和发现,从配置层开始解释每一层的作用和原理。
示例服务接口定义如下:
-
public interface CouponServiceViewFacade {
-
-
/**
-
* 查询单张优惠券
-
*/
-
CouponViewDTO query(String code);
-
}
二、配置层
2.1. 做什么
配置层提供配置处理工具类,在容器启动的时候,通过ServiceConfig.export实例化服务提供者,ReferenceConfig.get实例化服务消费者对象。
Dubbo应用使用spring容器启动时,Dubbo服务提供者配置处理器通过ServiceConfig.export启动Dubbo远程服务暴露本地服务。Dubbo服务消费者配置处理器通过ReferenceConfig.get实例化一个代理对象,并通过注册中心服务发现,连接远端服务提供者。
Dubbo配置可以使用注解和xml两种形式,本文采用注解的形式进行说明。
2.2. 怎么做
2.2.1 服务消费端的解析
Spring容器启动过程中,填充bean属性时,对含有Dubbo引用注解的属性使用org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.beans.factory.annotation.ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor进行初始化。如下是ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor的构造方法,Dubbo服务消费者注解处理器处理以下三个注解:DubboReference.class、Reference.class、com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference.class修饰的类。
ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类定义:
-
public class ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor extends AbstractAnnotationBeanPostProcessor implements
-
ApplicationContextAware {
-
-
public ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() {
-
super(DubboReference.class, Reference.class, com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference.class);
-
}
-
}
Dubbo服务发现到这一层,Dubbo即将开始构建服务消费者的代理对象,CouponServiceViewFacade接口的代理实现类。
2.2.2 服务提供端的解析
Spring容器启动的时候,加载注解@org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.context.annotation.DubboComponentScan指定范围的类,并初始化;初始化使用dubbo实现的扩展点org.apache.dubbo.config.spring.beans.factory.annotation.ServiceClassPostProcessor。
ServiceClassPostProcessor处理的注解类有DubboService.class,Service.class,com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service.class。
如下是ServiceClassPostProcessor类定义:
-
public class ServiceClassPostProcessor implements BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor, EnvironmentAware,
-
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanClassLoaderAware {
-
-
private final static List<Class<? extends Annotation>> serviceAnnotationTypes = asList(
-
DubboService.class,Service.class,com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Service.class
-
);
-
。。。
-
}
等待Spring容器ContextRefreshedEvent事件,启动Dubbo应用服务监听端口,暴露本地服务。
Dubbo服务注册到这一层,Dubbo即将开始构建服务提供者的代理对象,CouponServiceViewFacade实现类的反射代理类。
三、 代理层
3.1 做什么
为服务消费者生成代理实现实例,为服务提供者生成反射代理实例。
CouponServiceViewFacade的代理实现实例,消费端在调用query方法的时候,实际上是调用代理实现实例的query方法,通过他调用远程服务。
-
//
-
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
-
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
-
//
-
-
package org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode;
-
-
public class proxy1 implements DC, Destroyable, CouponServiceViewFacade, EchoService {
-
public static Method[] methods;
-
private InvocationHandler handler;
-
-
public proxy1(InvocationHandler var1) {
-
this.handler = var1;
-
}
-
-
public proxy1() {
-
}
-
-
public CouponViewDTO query(String var1) {
-
Object[] var2 = new Object[]{var1};
-
Object var3 = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], var2);
-
return (CouponViewDTO)var3;
-
}
-
}
CouponServiceViewFacade的反射代理实例,服务端接收到请求后,通过该实例的Invoke方法最终执行本地方法query。
-
/**
-
* InvokerWrapper
-
*/
-
public class AbstractProxyInvoker<CouponServiceViewFacade> implements Invoker<CouponServiceViewFacade> {
-
// 。。。
-
-
public AbstractProxyInvoker(CouponServiceViewFacade proxy, Class<CouponServiceViewFacade> type, URL url) {
-
//。。。
-
this.proxy = proxy;
-
this.type = type;
-
this.url = url;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
-
//。。。
-
Object value = doInvoke(proxy, invocation.getMethodName(), invocation.getParameterTypes(), invocation.getArguments());
-
//。。。
-
}
-
-
protected Object doInvoke(CouponServiceViewFacade proxy, String methodName, Class<?>[] parameterTypes, Object[] arguments) throws Throwable{
-
//。。。
-
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
-
}
-
-
}
3.2 怎么做
Dubbo代理工厂接口定义如下,定义了服务提供者和服务消费者的代理对象工厂方法。服务提供者代理对象和服务消费者代理对象都是通过工厂方法创建,工厂实现类可以通过SPI自定义扩展。
-
@SPI("javassist")
-
public interface ProxyFactory {
-
-
// 生成服务消费者代理对象
-
@Adaptive({PROXY_KEY})
-
<T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
-
-
// 生成服务消费者代理对象
-
@Adaptive({PROXY_KEY})
-
<T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, boolean generic) throws RpcException;
-
-
-
// 生成服务提供者代理对象
-
@Adaptive({PROXY_KEY})
-
<T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
-
-
}
3.2.1 服务消费者
3.2.1.1 创建服务消费者代理类
默认采用Javaassist代理工厂实现,Proxy.getProxy(interfaces)创建代理工厂类,newInstance创建具体代理对象。
-
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
-
-
@Override
-
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
-
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
-
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
-
}
-
-
。。。
-
-
}
3.2.1.2 服务消费者代理
Dubbo为每个服务消费者生成两个代理类:代理工厂类,接口代理类。
CouponServiceViewFacade代理工厂类:
-
public class Proxy1 extends Proxy implements DC {
-
public Proxy1() {
-
}
-
-
public Object newInstance(InvocationHandler var1) {
-
return new proxy1(var1);
-
}
-
}
最终生成的CouponServiceViewFacade的代理对象如下,其中handler的实现类是InvokerInvocationHandler,this.handler.invoke方法发起Dubbo调用。
-
//
-
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
-
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
-
//
-
-
package org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode;
-
-
public class proxy1 implements DC, Destroyable, CouponServiceViewFacade, EchoService {
-
public static Method[] methods;
-
private InvocationHandler handler;
-
-
public proxy1(InvocationHandler var1) {
-
this.handler = var1;
-
}
-
-
public proxy1() {
-
}
-
-
public CouponViewDTO query(String var1) {
-
Object[] var2 = new Object[]{var1};
-
Object var3 = this.handler.invoke(this, methods[0], var2);
-
return (CouponViewDTO)var3;
-
}
-
}
3.2.2 服务提供者
3.2.2.1 创建服务提供者代理类
默认Javaassist代理工厂实现,使用Wrapper包装本地服务提供者。proxy是实际的服务提供者实例,即CouponServiceViewFacade的本地实现类,type是接口类定义,URL是injvm协议URL。
-
public class JavassistProxyFactory extends AbstractProxyFactory {
-
-
。。。
-
-
@Override
-
public <T> Invoker<T> getInvoker(T proxy, Class<T> type, URL url) {
-
// 代理包装类,包装了本地的服务提供者
-
final Wrapper wrapper = Wrapper.getWrapper(proxy.getClass().getName().indexOf('$') < 0 ? proxy.getClass() : type);
-
// 代理类入口
-
return new AbstractProxyInvoker<T>(proxy, type, url) {
-
@Override
-
protected Object doInvoke(T proxy, String methodName,
-
Class<?>[] parameterTypes,
-
Object[] arguments) throws Throwable {
-
return wrapper.invokeMethod(proxy, methodName, parameterTypes, arguments);
-
}
-
};
-
}
-
-
}
3.2.2.2 Wrapper包装类
Dubbo为每个服务提供者的本地实现生成一个Wrapper代理类,抽象Wrapper类定义如下:
-
public abstract class Wrapper {
-
。。。
-
-
abstract public Object invokeMethod(Object instance, String mn, Class<?>[] types, Object[] args) throws NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException;
-
}
具体Wrapper代理类使用字节码技术动态生成,本地服务CouponServiceViewFacade的代理包装类举例:
-
//
-
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
-
// (powered by Fernflower decompiler)
-
//
-
-
package org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode;
-
-
import com.xxx.CouponServiceViewFacade;
-
import java.lang.reflect.InvocationTargetException;
-
import java.util.Map;
-
import org.apache.dubbo.common.bytecode.ClassGenerator.DC;
-
-
public class Wrapper25 extends Wrapper implements DC {
-
。。。
-
-
public Wrapper25() {
-
}
-
-
public Object invokeMethod(Object var1, String var2, Class[] var3, Object[] var4) throws InvocationTargetException {
-
CouponServiceViewFacade var5;
-
try {
-
var5 = (CouponServiceViewFacade)var1;
-
} catch (Throwable var8) {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException(var8);
-
}
-
-
try {
-
if ("query".equals(var2) && var3.length == 1) {
-
return var5.query((String)var4[0]);
-
}
-
} catch (Throwable var9) {
-
throw new InvocationTargetException(var9);
-
}
-
-
throw new NoSuchMethodException("Not found method \"" + var2 + "\" in class com.xxx.CouponServiceViewFacade.");
-
}
-
-
-
。。。
-
-
}
在服务初始化流程中,服务消费者代理对象生成后初始化就完成了,服务消费端的初始化顺序:ReferenceConfig.get->从注册中心订阅服务->启动客户端->创建DubboInvoker->构建ClusterInvoker→创建服务代理对象;
而服务提供端的初始化才刚开始,服务提供端的初始化顺序:ServiceConfig.export->创建AbstractProxyInvoker,通过Injvm协议关联本地服务->启动服务端→注册服务到注册中心。
四、注册层
4.1 做什么
封装服务地址的注册与发现,以服务 URL 为配置中心。服务提供者本地服务启动成功后,监听Dubbo端口成功后,通过注册协议发布到注册中心;服务消费者通过注册协议订阅服务,启动本地应用连接远程服务。
zookeeper://xxx/org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryService?application=xxx&...
4.2 怎么做
注册服务工厂接口定义如下,注册服务实现通过SPI扩展,默认是zk作为注册中心。
-
@SPI("dubbo")
-
public interface RegistryFactory {
-
-
@Adaptive({"protocol"})
-
Registry getRegistry(URL url);
-
-
}
注册服务接口定义;
-
public interface RegistryService {
-
-
-
void register(URL url);
-
-
-
void unregister(URL url);
-
-
-
void subscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener);
-
-
-
void unsubscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener);
-
-
-
List<URL> lookup(URL url);
-
-
}
五、集群层
5.1 做什么
服务消费方从注册中心订阅服务提供者后,将多个提供者包装成一个提供者,并且封装路由及负载均衡策略;并桥接注册中心,以 Invoker 为中心,扩展接口为 Cluster, Directory, Router, LoadBalance;
5.2 怎么做
5.2.1 Cluster
集群领域主要负责将多个服务提供者包装成一个ClusterInvoker,注入路由处理器链和负载均衡策略。主要策略有:failover、failfast、failsafe、failback、forking、available、mergeable、broadcast、zone-aware。
集群接口定义如下,只有一个方法:从服务目录中的多个服务提供者构建一个ClusterInvoker。
作用是对上层-代理层屏蔽集群层的逻辑;代理层调用服务方法只需执行Invoker.invoke,然后通过ClusterInvoker内部的路由策略和负载均衡策略计算具体执行哪个远端服务提供者。
-
@SPI(Cluster.DEFAULT)
-
public interface Cluster {
-
String DEFAULT = FailoverCluster.NAME;
-
-
@Adaptive
-
<T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException;
-
-
。。。
-
}
ClusterInvoker执行逻辑,先路由策略过滤,然后负载均衡策略选择最终的远端服务提供者。示例代理如下:
-
public abstract class AbstractClusterInvoker<T> implements ClusterInvoker<T> {
-
-
。。。
-
@Override
-
public Result invoke(final Invocation invocation) throws RpcException {
-
checkWhetherDestroyed();
-
-
// binding attachments into invocation.
-
Map<String, Object> contextAttachments = RpcContext.getContext().getObjectAttachments();
-
if (contextAttachments != null && contextAttachments.size() != 0) {
-
((RpcInvocation) invocation).addObjectAttachments(contextAttachments);
-
}
-
-
// 集群invoker执行时,先使用路由链过滤服务提供者
-
List<Invoker<T>> invokers = list(invocation);
-
LoadBalance loadbalance = initLoadBalance(invokers, invocation);
-
RpcUtils.attachInvocationIdIfAsync(getUrl(), invocation);
-
return doInvoke(invocation, invokers, loadbalance);
-
}
-
。。。
-
-
}
5.2.2 Directory
服务目录接口定义如下,Dubbo方法接口调用时,将方法信息包装成invocation,通过Directory.list过滤可执行的远端服务。
通过org.apache.dubbo.registry.integration.RegistryDirectory桥接注册中心,监听注册中心的路由配置修改、服务治理等事件。
-
public interface Directory<T> extends Node {
-
-
-
Class<T> getInterface();
-
-
List<Invoker<T>> list(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException;
-
-
List<Invoker<T>> getAllInvokers();
-
-
URL getConsumerUrl();
-
-
}
5.2.3 Router
从已知的所有服务提供者中根据路由规则刷选服务提供者。
服务订阅的时候初始化路由处理器链,调用远程服务的时候先使用路由链过滤服务提供者,再通过负载均衡选择具体的服务节点。
路由处理器链工具类,提供路由筛选服务,监听更新服务提供者。
-
public class RouterChain<T> {
-
-
。。。
-
-
public List<Invoker<T>> route(URL url, Invocation invocation) {
-
List<Invoker<T>> finalInvokers = invokers;
-
for (Router router : routers) {
-
finalInvokers = router.route(finalInvokers, url, invocation);
-
}
-
return finalInvokers;
-
}
-
-
/**
-
* Notify router chain of the initial addresses from registry at the first time.
-
* Notify whenever addresses in registry change.
-
*/
-
public void setInvokers(List<Invoker<T>> invokers) {
-
//路由链监听更新服务提供者
-
this.invokers = (invokers == null ? Collections.emptyList() : invokers);
-
routers.forEach(router -> router.notify(this.invokers));
-
}
-
-
}
订阅服务的时候,将路由链注入到RegistryDirectory中;
-
public class RegistryProtocol implements Protocol {
-
。。。
-
-
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) {
-
。。。
-
// 服务目录初始化路由链
-
directory.buildRouterChain(subscribeUrl);
-
directory.subscribe(toSubscribeUrl(subscribeUrl));
-
。。。
-
return registryInvokerWrapper;
-
}
-
-
。。。
-
-
}
5.2.4 LoadBalance
根据不同的负载均衡策略从可使用的远端服务实例中选择一个,负责均衡接口定义如下:
-
@SPI(RandomLoadBalance.NAME)
-
public interface LoadBalance {
-
-
@Adaptive("loadbalance")
-
<T> Invoker<T> select(List<Invoker<T>> invokers, URL url, Invocation invocation) throws RpcException;
-
-
}
六、监控层
6.1 做什么
监控RPC调用次数和调用时间,以Statistics为中心,扩展接口为 MonitorFactory, Monitor, MonitorService。
6.2 怎么做
监控工厂接口定义,通过SPI方式进行扩展;
-
@SPI("dubbo")
-
public interface MonitorFactory {
-
-
-
@Adaptive("protocol")
-
Monitor getMonitor(URL url);
-
-
}
监控服务接口定义如下,定义了一些默认的监控维度和指标项;
-
public interface MonitorService {
-
-
// 监控维度
-
-
String APPLICATION = "application";
-
-
String INTERFACE = "interface";
-
-
String METHOD = "method";
-
-
String GROUP = "group";
-
-
String VERSION = "version";
-
-
String CONSUMER = "consumer";
-
-
String PROVIDER = "provider";
-
-
String TIMESTAMP = "timestamp";
-
-
//监控指标项
-
-
String SUCCESS = "success";
-
-
String FAILURE = "failure";
-
-
String INPUT = INPUT_KEY;
-
-
String OUTPUT = OUTPUT_KEY;
-
-
String ELAPSED = "elapsed";
-
-
String CONCURRENT = "concurrent";
-
-
String MAX_INPUT = "max.input";
-
-
String MAX_OUTPUT = "max.output";
-
-
String MAX_ELAPSED = "max.elapsed";
-
-
String MAX_CONCURRENT = "max.concurrent";
-
-
void collect(URL statistics);
-
-
List<URL> lookup(URL query);
-
-
}
6.2.1 MonitorFilter
通过过滤器的方式收集服务的调用次数和调用时间,默认实现:
org.apache.dubbo.monitor.dubbo.DubboMonitor。
七、协议层
7.1 做什么
封装 RPC 调用,以 Invocation, Result 为中心,扩展接口为 Protocol, Invoker, Exporter。
1)Invocation是请求会话领域模型,每次请求有相应的Invocation实例,负责包装dubbo方法信息为请求参数;
2)Result是请求结果领域模型,每次请求都有相应的Result实例,负责包装dubbo方法响应;
3)Invoker是实体域,代表一个可执行实体,有本地、远程、集群三类;
4)Exporter服务提供者Invoker管理实体;
5)Protocol是服务域,管理Invoker的生命周期,提供服务的暴露和引用入口;
服务初始化流程中,从这一层开始进行远程服务的暴露和连接引用。
对于CouponServiceViewFacade服务来说,服务提供端会监听Dubbo端口启动tcp服务;服务消费端通过注册中心发现服务提供者信息,启动tcp服务连接远端提供者。
7.2 怎么做
协议接口定义如下,统一抽象了不同协议的服务暴露和引用模型,比如InjvmProtocol只需将Exporter,Invoker关联本地实现。DubboProtocol暴露服务的时候,需要监控本地端口启动服务;引用服务的时候,需要连接远端服务。
-
@SPI("dubbo")
-
public interface Protocol {
-
-
-
int getDefaultPort();
-
-
-
@Adaptive
-
<T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException;
-
-
-
@Adaptive
-
<T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException;
-
-
-
void destroy();
-
-
-
default List<ProtocolServer> getServers() {
-
return Collections.emptyList();
-
}
-
-
}
Invocation是RPC调用的会话对象,负责包装请求参数;Result是RPC调用的结果对象,负责包装RPC调用的结果对象,包括异常类信息;
-
public interface Invoker<T> extends Node {
-
-
-
Class<T> getInterface();
-
-
-
Result invoke(Invocation invocation) throws RpcException;
-
-
}
7.2.1 服务的暴露和引用
服务暴露的时候,开启RPC服务端;引用服务的时候,开启RPC客户端。
-
public class DubboProtocol extends AbstractProtocol {
-
-
。。。
-
-
@Override
-
public <T> Exporter<T> export(Invoker<T> invoker) throws RpcException {
-
。。。
-
// 开启rpc服务端
-
openServer(url);
-
optimizeSerialization(url);
-
-
return exporter;
-
}
-
-
@Override
-
public <T> Invoker<T> protocolBindingRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException {
-
optimizeSerialization(url);
-
-
// 创建dubbo invoker,开启rpc客户端
-
DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers);
-
invokers.add(invoker);
-
-
return invoker;
-
}
-
。。。
-
-
}
7.2.2 服务端响应请求
接收响应请求;
-
private ExchangeHandler requestHandler = new ExchangeHandlerAdapter() {
-
-
@Override
-
public CompletableFuture<Object> reply(ExchangeChannel channel, Object message) throws RemotingException {
-
。。。
-
Invocation inv = (Invocation) message;
-
Invoker<?> invoker = getInvoker(channel, inv);
-
-
RpcContext.getContext().setRemoteAddress(channel.getRemoteAddress());
-
//调用本地服务
-
Result result = invoker.invoke(inv);
-
return result.thenApply(Function.identity());
-
}
-
-
。。。
-
};
7.2.3 客户端发送请求
调用远程服务;
-
public class DubboInvoker<T> extends AbstractInvoker<T> {
-
-
。。。
-
-
@Override
-
protected Result doInvoke(final Invocation invocation) throws Throwable {
-
。。。
-
boolean isOneway = RpcUtils.isOneway(getUrl(), invocation);
-
int timeout = calculateTimeout(invocation, methodName);
-
if (isOneway) {
-
boolean isSent = getUrl().getMethodParameter(methodName, Constants.SENT_KEY, false);
-
currentClient.send(inv, isSent);
-
return AsyncRpcResult.newDefaultAsyncResult(invocation);
-
} else {
-
ExecutorService executor = getCallbackExecutor(getUrl(), inv);
-
CompletableFuture<AppResponse> appResponseFuture =
-
currentClient.request(inv, timeout, executor).thenApply(obj -> (AppResponse) obj);
-
FutureContext.getContext().setCompatibleFuture(appResponseFuture);
-
AsyncRpcResult result = new AsyncRpcResult(appResponseFuture, inv);
-
result.setExecutor(executor);
-
return result;
-
}
-
-
}
-
-
}
八、交换层
8.1 做什么
封装请求响应模式,同步转异步,以 Request, Response 为中心,扩展接口为 Exchanger, ExchangeChannel, ExchangeClient, ExchangeServer。
使用request包装Invocation作为完整的请求对象,使用response包装result作为完整的响应对象;Request、Response相比Invocation、Result添加了Dubbo的协议头。
8.2 怎么做
交换器对象接口定义,定义了远程服务的绑定和连接,使用SPI方式进行扩展;
-
@SPI(HeaderExchanger.NAME)
-
public interface Exchanger {
-
-
-
@Adaptive({Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY})
-
ExchangeServer bind(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
-
-
-
@Adaptive({Constants.EXCHANGER_KEY})
-
ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
-
-
}
8.2.1 服务提供者
服务提供端接收到请求后,本地执行,发送响应结果;
-
public class HeaderExchangeHandler implements ChannelHandlerDelegate {
-
-
-
。。。
-
-
-
void handleRequest(final ExchangeChannel channel, Request req) throws RemotingException {
-
//封装响应
-
Response res = new Response(req.getId(), req.getVersion());
-
。。。
-
Object msg = req.getData();
-
try {
-
CompletionStage<Object> future = handler.reply(channel, msg);
-
future.whenComplete((appResult, t) -> {
-
try {
-
if (t == null) {
-
res.setStatus(Response.OK);
-
res.setResult(appResult);
-
} else {
-
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
-
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(t));
-
}
-
channel.send(res);
-
} catch (RemotingException e) {
-
logger.warn("Send result to consumer failed, channel is " + channel + ", msg is " + e);
-
}
-
});
-
} catch (Throwable e) {
-
res.setStatus(Response.SERVICE_ERROR);
-
res.setErrorMessage(StringUtils.toString(e));
-
channel.send(res);
-
}
-
}
-
。。。
-
}
8.2.2 服务消费者
服务消费端发起请求的封装,方法执行成功后,返回一个future;
-
final class HeaderExchangeChannel implements ExchangeChannel {
-
-
。。。
-
-
//封装请求实体
-
@Override
-
public CompletableFuture<Object> request(Object request, int timeout, ExecutorService executor) throws RemotingException {
-
。。。
-
-
-
// create request.
-
Request req = new Request();
-
req.setVersion(Version.getProtocolVersion());
-
req.setTwoWay(true);
-
//RpcInvocation
-
req.setData(request);
-
DefaultFuture future = DefaultFuture.newFuture(channel, req, timeout, executor);
-
try {
-
channel.send(req);
-
} catch (RemotingException e) {
-
future.cancel();
-
throw e;
-
}
-
return future;
-
}
-
。。。
-
-
}
九、传输层
9.1 做什么
抽象传输层模型,兼容netty、mina、grizzly等通讯框架。
9.2 怎么做
传输器接口定义如下,它与交换器Exchanger接口定义相似,区别在于Exchanger是围绕Dubbo的Request和Response封装的操作门面接口,而Transporter更加的底层,Exchanger用于隔离Dubbo协议层和通讯层。
-
@SPI("netty")
-
public interface Transporter {
-
-
-
@Adaptive({Constants.SERVER_KEY, Constants.TRANSPORTER_KEY})
-
RemotingServer bind(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
-
-
-
@Adaptive({Constants.CLIENT_KEY, Constants.TRANSPORTER_KEY})
-
Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException;
-
-
}
通过SPI的方式,动态选择具体的传输框架,默认是netty;
-
public class Transporters {
-
-
。。。
-
-
public static RemotingServer bind(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers) throws RemotingException {
-
。。。
-
-
return getTransporter().bind(url, handler);
-
}
-
-
-
public static Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler... handlers) throws RemotingException {
-
。。。
-
return getTransporter().connect(url, handler);
-
}
-
-
public static Transporter getTransporter() {
-
return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
-
}
-
-
}
netty框架的channel适配如下,采用装饰模式,使用netty框架的channel作为Dubbo自定义的channel做实现;
-
final class NettyChannel extends AbstractChannel {
-
-
private NettyChannel(Channel channel, URL url, ChannelHandler handler) {
-
super(url, handler);
-
if (channel == null) {
-
throw new IllegalArgumentException("netty channel == null;");
-
}
-
this.channel = channel;
-
}
-
-
}
十、序列化
10.1 做什么
抽象序列化模型,兼容多种序列化框架,包括:fastjson、fst、hessian2、kryo、kryo2、protobuf等,通过序列化支持跨语言的方式,支持跨语言的RPC调用。
10.2 怎么做
定义Serialization扩展点,默认hessian2,支持跨语言。Serialization接口实际是一个工厂接口,通过SPI扩展;实际序列化和反序列化工作由ObjectOutput,ObjectInput完成,通过装饰模式让hessian2完成实际工作。
-
@SPI("hessian2")
-
public interface Serialization {
-
-
-
byte getContentTypeId();
-
-
-
String getContentType();
-
-
-
@Adaptive
-
ObjectOutput serialize(URL url, OutputStream output) throws IOException;
-
-
-
@Adaptive
-
ObjectInput deserialize(URL url, InputStream input) throws IOException;
-
-
}
10.2.1 通讯协议设计
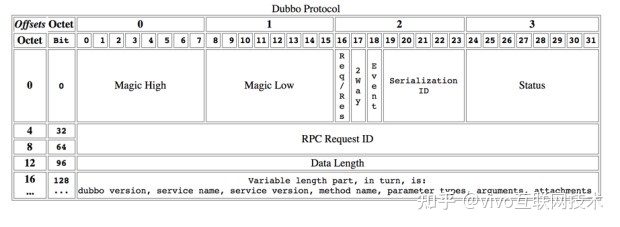
-
0-15bit表示Dubbo协议魔法数字,值:0xdabb;
-
16bit请求响应标记,Request - 1; Response - 0;
-
17bit请求模式标记,只有请求消息才会有,1表示需要服务端返回响应;
-
18bit是事件消息标记,1表示该消息是事件消息,比如心跳消息;
-
19-23bit是序列化类型标记,hessian序列化id是2,fastjson是6,详见org.apache.dubbo.common.serialize.Constants;
-
24-31bit表示状态,只有响应消息才有用;
-
32-64bit是RPC请求ID;
-
96-128bit是会话数据长度;
-
128是消息体字节序列;
十一、总结
Dubbo将RPC整个过程分成核心的代理层、注册层、集群层、协议层、传输层等,层与层之间的职责边界明确;核心层都通过接口定义,不依赖具体实现,这些接口串联起来形成了Dubbo的骨架;这个骨架也可以看作是Dubbo的内核,内核使用SPI 机制加载插件(扩展点),达到高度可扩展。
vivo互联网服务器团队-Wang Genfu
阅读(674) | 评论(0) | 转发(0) |