6. 使用getResponse方法获得WebService方法的返回结果,代码如下:
| 1 | SoapObject soapObject = (SoapObject) envelope.getResponse(); |
示例:通过WebService查询产品信息
本例涉及到一个WebService服务端程序和一个OPhone客户端程序。读者可直接将服务端程序(axis2目录)复制到\webapps目录中,然后启动Tomcat,并在浏览器地址栏中输入如下的URL:
http://localhost:8080/axis2
如果在浏览器中显示如图2所示的页面,说明服务端程序已经安装成功。
图2 WebService主页面
这个服务端WebService程序是SearchProductService,实际上SearchProductService是一个Java类,只 是利用Axis2将其映射成WebService。在该类中有一个getProduct方法。这个方法有一个String类型的参数,表示产品名称。该方 法返回一个Product对象,该对象有3个属性:name、price和productNumber。读者可以使用如下的URL来查看 SearchProductService的WSDL文档。
http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/SearchProductService?wsdl
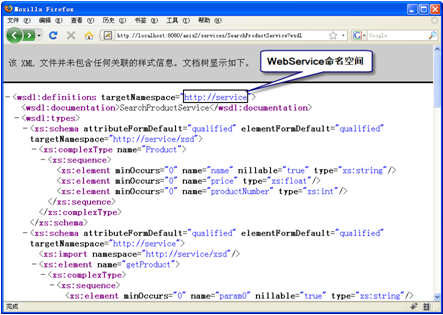
显示WSDL文档的页面如图3所示。
图3 WSDL文档
在图3中的黑框中就是WebService的命名空间,也是SoapObject类的构造方法的第1个参数值。这个WebService程序可以直接使用如下的URL进行测试。
http://localhost:8080/axis2/services/SearchProductService/getProduct?param0=iphone
测试的结果如图4所示。
图4 测试getProduct方法
从图4所示的测试结果可以看出,Axis2将getProduct方法返回的Product对象直接转换成了XML文档(实际上是SOAP格式)返回。
下面我们来根据前面介绍的使用KSOAP2的步骤来编写调用WebService的OPhone客户端程序,代码如下:
| 01 | package net.blogjava.mobile.wsclient; |
| 03 | import org.ksoap2.SoapEnvelope; |
| 04 | import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject; |
| 05 | import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapSerializationEnvelope; |
| 06 | import org.ksoap2.transport.HttpTransportSE; |
| 07 | import android.app.Activity; |
| 08 | import android.os.Bundle; |
| 09 | import android.view.View; |
| 10 | import android.view.View.OnClickListener; |
| 11 | import android.widget.Button; |
| 12 | import android.widget.EditText; |
| 13 | import android.widget.TextView; |
| 15 | public class Main extends Activity implements OnClickListener |
| 18 | public void onClick(View view) |
| 20 | EditText etProductName = (EditText)findViewById(R.id.etProductName); |
| 21 | TextView tvResult = (TextView)findViewById(R.id.tvResult); |
| 22 | // WSDL文档的URL,192.168.17.156为PC的ID地址 |
| 23 | String serviceUrl = "http://192.168.17.156:8080/axis2/services/SearchProductService?wsdl"; |
| 25 | String methodName = "getProduct"; |
| 26 | // 第1步:创建SoapObject对象,并指定WebService的命名空间和调用的方法名 |
| 27 | SoapObject request = new SoapObject("http://service", methodName); |
| 28 | // 第2步:设置WebService方法的参数 |
| 29 | request.addProperty("productName", etProductName.getText().toString()); |
| 30 | // 第3步:创建SoapSerializationEnvelope对象,并指定WebService的版本 |
| 31 | SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope(SoapEnvelope.VER11); |
| 33 | envelope.bodyOut = request; |
| 34 | // 第4步:创建HttpTransportSE对象,并指定WSDL文档的URL |
| 35 | HttpTransportSE ht = new HttpTransportSE(serviceUrl); |
| 39 | ht.call(null, envelope); |
| 40 | if (envelope.getResponse() != null) |
| 42 | // 第6步:使用getResponse方法获得WebService方法的返回结果 |
| 43 | SoapObject soapObject = (SoapObject) envelope.getResponse(); |
| 44 | // 通过getProperty方法获得Product对象的属性值 |
| 45 | String result = "产品名称:" + soapObject.getProperty("name") + "\n"; |
| 46 | result += "产品数量:" + soapObject.getProperty("productNumber") + "\n"; |
| 47 | result += "产品价格:" + soapObject.getProperty("price"); |
| 48 | tvResult.setText(result); |
| 52 | tvResult.setText("无此产品."); |
| 60 | public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) |
| 62 | super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); |
| 63 | setContentView(R.layout.main); |
| 64 | Button btnSearch = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSearch); |
| 65 | btnSearch.setOnClickListener(this); |
在编写上面代码时应注意如下两点:
- 在 第2步中addProperty方法的第1个参数值是productName,该值虽然是getProduct方法的参数名,但addProperty方 法的第1个参数值并不限于productName,读者可以将这个参数设为其他的任何字符串(但该值必须在XML中是合法的,例如,不是设为 “<”、“>”等XML预留的字符串)。
- 通过SoapObject类的getProperty方法可以获得Product对象的属性值,这些属性名就是图4所示的测试结果中的属性名。
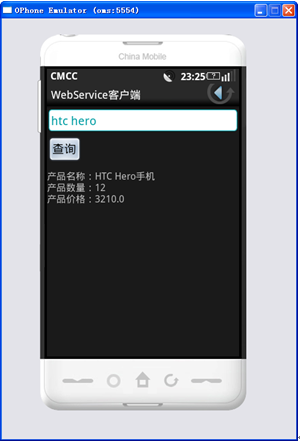
运行本例,在文本框中输入“htc hero”,单击【查询】按钮,会在按钮下方显示如图5所示的查询结果。
图5 显示查询结果
防止UI组件阻塞
从功能上看,本文示例中给出的代码并没有任何问题。但可能有的读者会有这样的担心:如果调用WebService的用户很多,至使服务端响应迟缓;或服务 端的IP根本就不对,那么在这些情况下,用户界面的按钮和文本框组件岂不是象“死”了一样无法响应用户的其他动作。当然,发生这种情况的可能性是有的,尤 其是在复杂的网络环境中发生的可能性是很大的,一但发生这种事情,就会使整个软件系统在用户体验上变得非常糟糕。
用户和开发人员都希望改善这种糟糕的情况。最理想的状态是单击按钮调用WebService方法时,即使由于某种原因,WebService方法并未立即返回,界面上的组件仍然会处于活动状态,也就是说,用户仍然可以使用当前界面中的其他组件。
在OPhone中可以采用异步的方式来达到这个目的。异步实际上就是通过多线程的方式来实现。一般使用new Thread(this).start()来创建和开始一个线程。但本节并不使用Thread来实现异步,而是通过AsyncTask类使要执行的任务 (调用WebService)在后台执行。
下面先看看改进后的代码。
| 01 | package net.blogjava.mobile.wsclient; |
| 03 | import org.ksoap2.SoapEnvelope; |
| 04 | import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapObject; |
| 05 | import org.ksoap2.serialization.SoapSerializationEnvelope; |
| 06 | import org.ksoap2.transport.HttpTransportSE; |
| 07 | import android.app.Activity; |
| 08 | import android.os.AsyncTask; |
| 09 | import android.os.Bundle; |
| 10 | import android.view.View; |
| 11 | import android.view.View.OnClickListener; |
| 12 | import android.widget.Button; |
| 13 | import android.widget.EditText; |
| 14 | import android.widget.TextView; |
| 16 | public class Main extends Activity implements OnClickListener |
| 18 | private EditText etProductName; |
| 19 | private TextView tvResult; |
| 21 | class WSAsyncTask extends AsyncTask |
| 25 | protected Object doInBackground(Object... params) |
| 29 | String serviceUrl = "http://192.168.17.156:8080/axis2/services/SearchProductService?wsdl"; |
| 30 | String methodName = "getProduct"; |
| 31 | SoapObject request = new SoapObject("http://service", |
| 33 | request.addProperty("productName", etProductName.getText().toString()); |
| 34 | SoapSerializationEnvelope envelope = new SoapSerializationEnvelope( |
| 36 | envelope.bodyOut = request; |
| 37 | HttpTransportSE ht = new HttpTransportSE(serviceUrl); |
| 39 | ht.call(null, envelope); |
| 40 | if (envelope.getResponse() != null) |
| 42 | SoapObject soapObject = (SoapObject) envelope.getResponse(); |
| 43 | result = "产品名称:" + soapObject.getProperty("name") + "\n"; |
| 44 | result += "产品数量:" + soapObject.getProperty("productNumber") |
| 46 | result += "产品价格:" + soapObject.getProperty("price"); |
| 56 | result = "调用WebService错误."; |
| 59 | tvResult.post(new Runnable() |
| 64 | tvResult.setText(result); |
| 73 | public void onClick(View view) |
| 75 | // 异步执行调用WebService的任务 |
| 76 | new WSAsyncTask().execute(); |
| 79 | public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) |
| 81 | super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); |
| 82 | setContentView(R.layout.main); |
| 83 | Button btnSearch = (Button) findViewById(R.id.btnSearch); |
| 84 | btnSearch.setOnClickListener(this); |
| 85 | etProductName = (EditText) findViewById(R.id.etProductName); |
| 86 | tvResult = (TextView) findViewById(R.id.tvResult); |
调用WebService的核心代码与示例中的代码完全一样,在这里就不再做具体的介绍了。但在编写上面的代码时还需要注意如下几点。
1. 一般需要编写一个AsyncTask的子类来完成后台执行任务的工作。
2. AsyncTask的核心方法是doInBackground,当调用AsyncTask类的execute方法时,doInBackground方法会异步执行。因此,可以将执行任务的代码写在doInBackground方法中。
3. 由 于本例中的TextView组件是在主线程(UI线程)中创建的,因此,在其他的线程(doInBackground方法所在的线程)中不能直接更新 TextVew组件。为了更新TextView组件,需要使用TextView类的post方法。该方法的参数是一个Runnable对象,需要将更新 TextView组件的代码写在Runnable接口的run方法中。
4. 虽然不能在其他线程中更新UI组件,但可以从其他线程直接读取UI组件的值。例如,在doInBackground方法中直接读取了EditText组件的值。
5. 调用AsyncTask类的execute方法后会立即返回。execute方法的参数就是doInBackground方法的参数。doInBackground方法的返回值可以通过AsyncTask.execute(...).get()方法获得。
读者可以将本例中的IP改成其他的值,看看单击按钮后,是否还可在文本框中输入其他的内容。如果这个IP是正确的,并且WebService可访问,那么会在TextView组件中输出相应的返回值。
总结
本文主要介绍了如何使用KSOAP2来调用WebService。KSOAP2是第三方开发的专门用于在移动设备调用WebService的类库。使用 KSOAP2调用WebService可分为6步来完成,其中主要使用了SoapObject对象来指定了要调用的方法,然后通过 HttpTransportSE对象的call方法来调用WebService的方法,最后通过getResponse方法返回结果。读者可以通过本文提 供的完整示例来体会使用KSOAP2调用WebService的完整过程。在最后还介绍了如何通过异步调用WebService的方式来防止因服务端故障 或其他原因导致的UI组件阻塞。