http://blog.csdn.net/mu0206mu/article/details/7465514
http://blog.csdn.net/huangyabin001/article/category/2703721
Android系统Recovery工作原理之使用update.zip升级过程分析(七)---Recovery服务的核心install_package函数
一、 Recovery服务的核心install_package(升级update.zip特有)
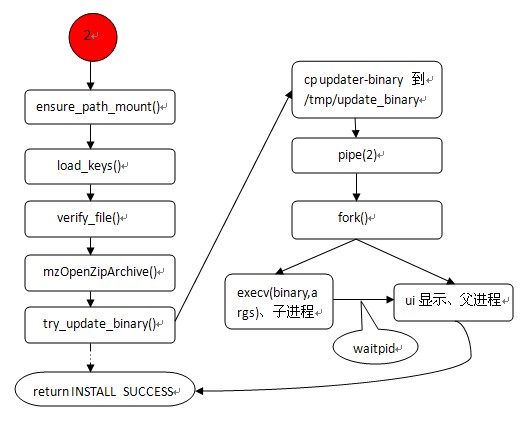
和Recovery服务中的wipe_data、wipe_cache不同,install_package()是升级update.zip特有的一部分,也是最核心的部分。在这一步才真正开始对我们的update.zip包进行处理。下面就开始分析这一部分。还是先看图例:
这一部分的源码文件位于:/gingerbread0919/bootable/recovery/install.c。这是一个没有main函数的源码文件,还是把源码先贴出来如下:
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
#include
-
-
#include "common.h"
-
#include "install.h"
-
#include "mincrypt/rsa.h"
-
#include "minui/minui.h"
-
#include "minzip/SysUtil.h"
-
#include "minzip/Zip.h"
-
#include "mtdutils/mounts.h"
-
#include "mtdutils/mtdutils.h"
-
#include "roots.h"
-
#include "verifier.h"
-
-
#define ASSUMED_UPDATE_BINARY_NAME "META-INF/com/google/android/update-binary"
-
#define PUBLIC_KEYS_FILE "/res/keys"
-
-
-
static int
-
try_update_binary(const char *path, ZipArchive *zip) {
-
const ZipEntry* binary_entry =
-
mzFindZipEntry(zip, ASSUMED_UPDATE_BINARY_NAME);
-
if (binary_entry == NULL) {
-
mzCloseZipArchive(zip);
-
return INSTALL_CORRUPT;
-
}
-
-
char* binary = "/tmp/update_binary";
-
unlink(binary);
-
int fd = creat(binary, 0755);
-
if (fd < 0) {
-
mzCloseZipArchive(zip);
-
LOGE("Can't make %s\n", binary);
-
return 1;
-
}
-
bool ok = mzExtractZipEntryToFile(zip, binary_entry, fd);
-
close(fd);
-
mzCloseZipArchive(zip);
-
-
if (!ok) {
-
LOGE("Can't copy %s\n", ASSUMED_UPDATE_BINARY_NAME);
-
return 1;
-
}
-
-
int pipefd[2];
-
pipe(pipefd);
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
char** args = malloc(sizeof(char*) * 5);
-
args[0] = binary;
-
args[1] = EXPAND(RECOVERY_API_VERSION);
-
args[2] = malloc(10);
-
sprintf(args[2], "%d", pipefd[1]);
-
args[3] = (char*)path;
-
args[4] = NULL;
-
-
pid_t pid = fork();
-
if (pid == 0) {
-
close(pipefd[0]);
-
execv(binary, args);
-
fprintf(stdout, "E:Can't run %s (%s)\n", binary, strerror(errno));
-
_exit(-1);
-
}
-
close(pipefd[1]);
-
-
char buffer[1024];
-
FILE* from_child = fdopen(pipefd[0], "r");
-
while (fgets(buffer, sizeof(buffer), from_child) != NULL) {
-
char* command = strtok(buffer, " \n");
-
if (command == NULL) {
-
continue;
-
} else if (strcmp(command, "progress") == 0) {
-
char* fraction_s = strtok(NULL, " \n");
-
char* seconds_s = strtok(NULL, " \n");
-
-
float fraction = strtof(fraction_s, NULL);
-
int seconds = strtol(seconds_s, NULL, 10);
-
-
ui_show_progress(fraction * (1-VERIFICATION_PROGRESS_FRACTION),
-
seconds);
-
} else if (strcmp(command, "set_progress") == 0) {
-
char* fraction_s = strtok(NULL, " \n");
-
float fraction = strtof(fraction_s, NULL);
-
ui_set_progress(fraction);
-
} else if (strcmp(command, "ui_print") == 0) {
-
char* str = strtok(NULL, "\n");
-
if (str) {
-
ui_print("%s", str);
-
} else {
-
ui_print("\n");
-
}
-
} else {
-
LOGE("unknown command [%s]\n", command);
-
}
-
}
-
fclose(from_child);
-
-
int status;
-
waitpid(pid, &status, 0);
-
if (!WIFEXITED(status) || WEXITSTATUS(status) != 0) {
-
LOGE("Error in %s\n(Status %d)\n", path, WEXITSTATUS(status));
-
return INSTALL_ERROR;
-
}
-
-
return INSTALL_SUCCESS;
-
}
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
-
static RSAPublicKey*
-
load_keys(const char* filename, int* numKeys) {
-
RSAPublicKey* out = NULL;
-
*numKeys = 0;
-
-
FILE* f = fopen(filename, "r");
-
if (f == NULL) {
-
LOGE("opening %s: %s\n", filename, strerror(errno));
-
goto exit;
-
}
-
-
int i;
-
bool done = false;
-
while (!done) {
-
++*numKeys;
-
out = realloc(out, *numKeys * sizeof(RSAPublicKey));
-
RSAPublicKey* key = out + (*numKeys - 1);
-
if (fscanf(f, " { %i , 0x%x , { %u",
-
&(key->len), &(key->n0inv), &(key->n[0])) != 3) {
-
goto exit;
-
}
-
if (key->len != RSANUMWORDS) {
-
LOGE("key length (%d) does not match expected size\n", key->len);
-
goto exit;
-
}
-
for (i = 1; i < key->len; ++i) {
-
if (fscanf(f, " , %u", &(key->n[i])) != 1) goto exit;
-
}
-
if (fscanf(f, " } , { %u", &(key->rr[0])) != 1) goto exit;
-
for (i = 1; i < key->len; ++i) {
-
if (fscanf(f, " , %u", &(key->rr[i])) != 1) goto exit;
-
}
-
fscanf(f, " } } ");
-
-
-
switch (fgetc(f)) {
-
case ',':
-
-
break;
-
-
case EOF:
-
done = true;
-
break;
-
-
default:
-
LOGE("unexpected character between keys\n");
-
goto exit;
-
}
-
}
-
-
fclose(f);
-
return out;
-
-
exit:
-
if (f) fclose(f);
-
free(out);
-
*numKeys = 0;
-
return NULL;
-
}
-
-
int
-
install_package(const char *path)
-
{
-
ui_set_background(BACKGROUND_ICON_INSTALLING);
-
ui_print("Finding update package...\n");
-
ui_show_indeterminate_progress();
-
LOGI("Update location: %s\n", path);
-
-
if (ensure_path_mounted(path) != 0) {
-
LOGE("Can't mount %s\n", path);
-
return INSTALL_CORRUPT;
-
}
-
-
ui_print("Opening update package...\n");
-
-
int numKeys;
-
RSAPublicKey* loadedKeys = load_keys(PUBLIC_KEYS_FILE, &numKeys);
-
if (loadedKeys == NULL) {
-
LOGE("Failed to load keys\n");
-
return INSTALL_CORRUPT;
-
}
-
LOGI("%d key(s) loaded from %s\n", numKeys, PUBLIC_KEYS_FILE);
-
-
-
ui_print("Verifying update package...\n");
-
ui_show_progress(
-
VERIFICATION_PROGRESS_FRACTION,
-
VERIFICATION_PROGRESS_TIME);
-
-
int err;
-
err = verify_file(path, loadedKeys, numKeys);
-
free(loadedKeys);
-
LOGI("verify_file returned %d\n", err);
-
if (err != VERIFY_SUCCESS) {
-
LOGE("signature verification failed\n");
-
return INSTALL_CORRUPT;
-
}
-
-
-
-
ZipArchive zip;
-
err = mzOpenZipArchive(path, &zip);
-
if (err != 0) {
-
LOGE("Can't open %s\n(%s)\n", path, err != -1 ? strerror(err) : "bad");
-
return INSTALL_CORRUPT;
-
}
-
-
-
-
ui_print("Installing update...\n");
-
return try_update_binary(path, &zip);
-
}
下面顺着上面的流程图和源码来分析这一流程:
①ensure_path_mount():先判断所传的update.zip包路径所在的分区是否已经挂载。如果没有则先挂载。
②load_keys():加载公钥源文件,路径位于/res/keys。这个文件在Recovery镜像的根文件系统中。
③verify_file():对升级包update.zip包进行签名验证。
④mzOpenZipArchive():打开升级包,并将相关的信息拷贝到一个临时的ZipArchinve变量中。这一步并未对我们的update.zip包解压。
⑤try_update_binary():在这个函数中才是对我们的update.zip升级的地方。这个函数一开始先根据我们上一步获得的zip包信息,以及升级包的绝对路径将update_binary文件拷贝到内存文件系统的/tmp/update_binary中。以便后面使用。
⑥pipe():创建管道,用于下面的子进程和父进程之间的通信。
⑦fork():创建子进程。其中的子进程主要负责执行binary(execv(binary,args),即执行我们的安装命令脚本),父进程负责接受子进程发送的命令去更新ui显示(显示当前的进度)。子父进程间通信依靠管道。
⑧其中,在创建子进程后,父进程有两个作用。一是通过管道接受子进程发送的命令来更新UI显示。二是等待子进程退出并返回INSTALL SUCCESS。其中子进程在解析执行安装脚本的同时所发送的命令有以下几种:
progress :根据第二个参数secs(秒)来设置进度条。
set_progress :直接设置进度条,frac取值在0.0到0.1之间。
firmware <”hboot”|”radio”>:升级firmware时使用,在API V3中不再使用。
ui_print :在屏幕上显示字符串,即打印更新过程。
execv(binary,args)的作用就是去执行binary程序,这个程序的实质就是去解析update.zip包中的updater-script脚本中的命令并执行。由此,Recovery服务就进入了实际安装update.zip包的过程。
下一篇继续分析使用update-binary解析并执行updater-script的过程。
阅读(2616) | 评论(0) | 转发(0) |
