转自:http://blog.yufeng.info/archives/2234
我们在做网络服务器的时候,通常会很关心网络的带宽和延迟。因为我们的很多协议都是request-reponse协议,延迟决定了最大的QPS,而带宽决定了最大的负荷。 通常我们知道自己的网卡是什么型号,交换机什么型号,主机之间的物理距离是多少,理论上是知道带宽和延迟是多少的。但是现实的情况是,真正的带宽和延迟情况会有很多变数的,比如说网卡驱动,交换机跳数,丢包率,协议栈配置,光实际速度都很大的影响了数值的估算。 所以我们需要找到工具来实际测量下。
网络测量的工具有很多,netperf什么的都很不错。 我这里推荐了qperf,这是RHEL 6发行版里面自带的,所以使用起来很方便,只要简单的:
yum install qperf
我们看下man qperf的介绍:
-
qperf measures bandwidth and latency between two nodes. It can work over TCP/IP as well as the RDMA transports. On one of the nodes, qperf is typically run with no arguments designating it the server node. One may then run qperf on a client node to obtain measurements such as bandwidth, latency and cpu utilization.
-
In its most basic form, qperf is run on one node in server mode by invoking it with no arguments. On the other node, it is run with two arguments: the name of the server node followed by the name of the test. A list of tests can be found in the section, TESTS. A variety of options may also be specified.
使用起来也相当简单:
在其中一台机器上运行qperf,不带任何参数就好,这台机器就充当服务器角色:
-
$ uname -r
-
2.6.32-131.21.1.tb477.el6.x86_64
-
$ qperf
在另外一台机器上运行qperf,测量tcp的带宽和延时,顺便看下双方机器的配置况:
-
$ qperf 10.232.64.yyy tcp_bw tcp_lat conf
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 118 MB/sec
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 31.9 us
-
conf:
-
loc_node = xxx.sqa.cm4
-
loc_cpu = 16 Cores: Intel Xeon L5630 @ 2.13GHz
-
loc_os = Linux 2.6.32-131.21.1.tb477.el6.x86_64
-
loc_qperf = 0.4.6
-
rem_node = yyy.sqa.cm4
-
rem_cpu = 16 Cores: Intel Xeon L5630 @ 2.13GHz
-
rem_os = Linux 2.6.32-131.21.1.tb477.el6.x86_64
-
rem_qperf = 0.4.6
是不是很方便?典型情况下我们的带宽是118M,延迟是32us, 在标准的千M环境下是符合预期的。
当然qperf有很多高级参数,可以设置socket buffer的大小,绑定CPU亲缘性等, 很赞的一个特性是可以通过持续改变某个重要参数的值,来观察临界点:
-
-oo, –loop Var:Init:Last:Incr
-
Run a test multiple times sequencing through a series of values. Var is the loop variable;
-
Init is the initial value; Last is the value it must not exceed and Incr is the increment. It
-
is useful to set the –verbose_used (-vu) option in conjunction with this option.
比如我们可以透过改变消息的大小(msg_size),比如从1个字节到64K,每次倍增的方式,来观察带宽和延迟的变化情况,演示下:
-
$ qperf -oo msg_size:1:64K:*2 10.232.64.yyy tcp_bw tcp_lat
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 2.43 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 4.69 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 9.12 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 18.5 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 33.1 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 61.4 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 114 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 118 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 113 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 114 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 114 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 118 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 117 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 118 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 118 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 117 MB/sec
-
tcp_bw:
-
bw = 117 MB/sec
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 31 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 31.1 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 31.1 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 31.4 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 30.8 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 32.1 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 32.6 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 33.3 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 35.5 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 38.6 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 50.1 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 69.6 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 88 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 128 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 209 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 365 us
-
tcp_lat:
-
latency = 650 us
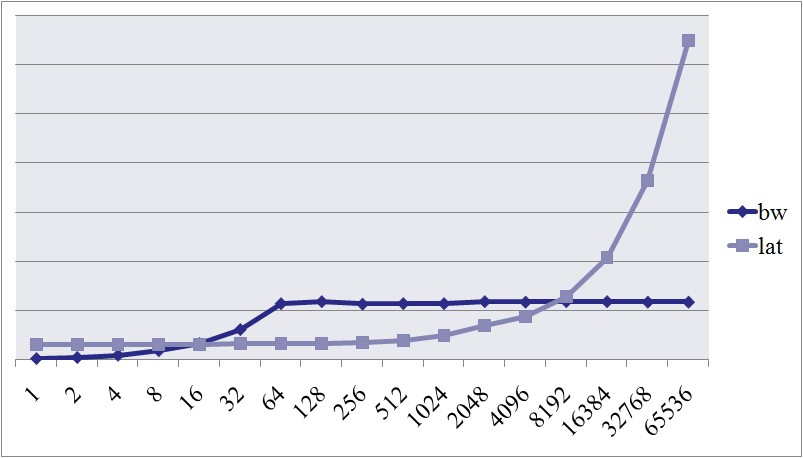
我们可以看到当包的大小达到64字节的时候,带宽就上不去了;包到达1K的时候,延迟有了很大的变化。 这些临界点对我们的服务器编程时候对性能的估计和预期非常有帮助。
qperf除了测量tcp的,还可以测试rdma, udp, sctp等主流网络协议的带宽和延迟,算是个很新的工具,推荐大家使用。
阅读(3142) | 评论(0) | 转发(0) |
