分类: Oracle
2019-02-10 15:04:24
|
|
|
|
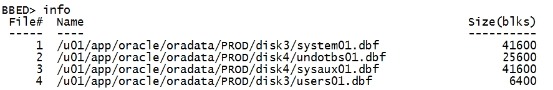
一.1 相关知识点扫盲 BBED(Oracle Block Browerand EDitor Tool),用来直接查看和修改数据文件数据的一个工具,是Oracle一款内部工具,可以直接修改Oracle数据文件块的内容,在一些极端恢复场景下比较有用。该工具不受Oracle支持,所以默认是没有生成可执行文件的,在使用前需要重新连接。 一.1.1 我的编译代码 ls -l $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib/*sbbd* ls -l $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/mesg/bbed* chown oracle:dba /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/rdbms/lib/*sbbd* chown oracle:dba /u01/app/oracle/product/11.2.0/dbhome_1/rdbms/mesg/bbed* --cd $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib --make -f ins_rdbms.mk $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib/bbed --make -f $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib/ins_rdbms.mk $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib/bbed make -f $ORACLE_HOME/rdbms/lib/ins_rdbms.mk BBED=$ORACLE_HOME/bin/bbed $ORACLE_HOME/bin/bbed 一.1.2 我的使用代码 vi /home/oracle/file.txt set line 9999 pagesize 9999 col name format a80 select file#||' '||name||' '||bytes name from v$datafile; vi /home/oracle/bbed.par blocksize=8192 listfile=/home/oracle/file.txt mode=edit bbed parfile=/home/oracle/bbed.par bbed PASSWORD=blockedit mode=edit blocksize=8192 listfile=/home/oracle/file.txt 一.1.3 注意事项 ① 若使用bbed的过程中,数据库有重启的过程,最好是退出BBED重新进入bbed的环境 ② windows下BBED软件和其他系统下BBED不太一样,操作的时候块号比其他系统下多一个 一.2 bbed日志记录 log.bbd bbed启动和运行的过程会将运行过的所有命令记录到当前的目录下log.bbd文件中,所以bbed要求oracle用户在当前目录具有创建文件的权限。 一.3 报错 一.3.1 BBED-00303: unable to open file 'log.bbd' oracle用户需要对当前操作目录有权限,否则报错: [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/oracle>bbed BBED-00303: unable to open file 'log.bbd' [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/oracle>touch log.bbd touch: 0652-046 Cannot create log.bbd. [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/oracle>ls -ld drwxr-xr-x 5 root dba 256 Mar 14 15:41 . [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/oracle>cd /home/oracle [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/home/oracle>ls -ld drwxr-xr-x 3 oracle dba 256 Apr 05 17:01 . [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/home/oracle>bbed Password: BBED-00113: Invalid password. Please rerun utility with the correct password. [ZFZHLHRDB2:oracle]:/home/oracle>bbed parfile=/home/oracle/bbed.par Password: BBED: Release 2.0.0.0.0 - Limited Production on Tue Apr 5 17:28:35 2016 Copyright (c) 1982, 2011, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. ************* !!! For Oracle Internal Use only !!! *************** BBED> info File# Name Size(blks) ----- ---- ---------- 1 /oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/system01.dbf 96000 2 /oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/sysaux01.dbf 62720 3 /oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/undotbs01.dbf 11520 4 /oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/users01.dbf 640 5 /oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/example01.dbf 40080 第二章 BBED基本命令 先看帮助的说明: BBED> help all SET DBA [ dba | file#, block# ] SET FILENAME 'filename' SET FILE file# SET BLOCK [+/-]block# SET OFFSET [ [+/-]byte offset | symbol |*symbol ] SET BLOCKSIZE bytes SET LIST[FILE] 'filename' SET WIDTH character_count SET COUNT bytes_to_display SET IBASE [ HEX | OCT | DEC ] SET OBASE [ HEX | OCT | DEC ] SET MODE [ BROWSE | EDIT ] SET SPOOL [ Y | N ] SHOW [ INFO MAP[/v] [ DBA | FILENAME | FILE | BLOCK ] DUMP[/v] [ DBA | FILENAME | FILE | BLOCK |OFFSET | COUNT ] PRINT[/x|d|u|o|c] [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME |BLOCK | OFFSET | symbol | *symbol ] EXAMINE[/Nuf] [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME |BLOCK | OFFSET | symbol | *symbol ] < /Nuf>: N - a number which specifies a repeatcount. u - a letter which specifies a unit size: b -b1, ub1 (byte) h -b2, ub2 (half-word) w -b4, ub4(word) r -Oracle table/index row f - a letter which specifies a displayformat: x -hexadecimal d -decimal u -unsigned decimal o -octal c -character (native) n -Oracle number t -Oracle date i -Oracle rowid FIND[/x|d|u|o|c] numeric/character string [TOP | CURR ] COPY [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK ] TO [DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK ] MODIFY[/x|d|u|o|c] numeric/character string [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK | OFFSET | symbol | *symbol ] ASSIGN[/x|d|u|o] < target spec> : [ DBA | FILE |FILENAME | BLOCK | OFFSET | symbol | *symbol ] < source spec> : [ value | SUM [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK ] [APPLY ] PUSH [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK |OFFSET ] POP [ALL] REVERT [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK ] UNDO HELP [ VERIFY [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK ] CORRUPT [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK ] 下面是几个常用的: set 设定当前的环境 show 查看当前的环境参数,跟sqlplus的同名命令类似。 dump 列出指定block的内容 find 在指定的block中查找指定的字符串,结果是显示出字符串,及其偏移量--offset,偏移量就是在block中的字节数 modify 修改指定block的指定偏移量的值,可以在线修改。 copy 把一个block的内容copy到另一个block中 verify 检查当前环境是否有坏块 sum 计算block的checksum,modify之后block就被标识为坏块,current checksum与reqired checksum不一致,sum命令可以计算出新的checksum并应用到当前块。 undo 回滚当前的修改操作,如果手误做错了,undo一下就ok了,回到原来的状态。 revert 回滚所有之前的修改操作,意思就是 undo all 二.1 SET 命令 二.1.1 set dba Set the current data block using the standard Oracle DBA (Data Block Address)format. This is entered as file_id, block. 关于DBA 说明,参考:Oracle rdba和 dba 说明 http://blog.csdn.net/tianlesoftware/article/details/6529346 select rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid)rel_fno, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid)blockno, dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) rowno from scott.emp; |

|
|
set dba 4,145 |

|
|
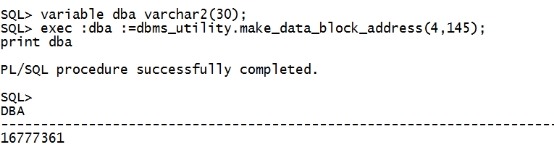
如果设置成功,会返回该block的RDBA (Relative Data Block Address),rdba就是rowid中的rfile#+block#。括号里面的是DBA值和block 和 file id。 我们验证一下: sqlplus执行: variable dba varchar2(30); exec :dba :=dbms_utility.make_data_block_address(4,145); print dba |
|
|
二.1.2 set filename Sets the current file to the one specified. It must be a valid Oracle data file andit must be enclosed in single quotes. If the file is not in the current path itmust also be fully qualified. If successful, bbed will respond showing the filenow being accessed. BBED> set filename '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/dave2/users01.dbf' FILENAME /u01/app/oracle/oradata/dave2/users01.dbf --必须是一个有效的datafile,并且用单引号括起来 二.1.3 set file Sets the current file to the number specified. The number specified must be one ofthe file ids supplied in the filelist referenced at startup. If successful,bbed will respond showing the file id now being accessed. BBED> set file 4 FILE# 4 --注意这里的number,是我们之前配置的filelist里的number。它可以和我们db 里的file id 不一样。 不过最好是配置一样的。 二.1.4 set block Sets the current block. The block is relative to the filename or file already set.The absolute block can be specified, or an offset to the current block can bespecified using the plus (+) or (-) symbols. If successful, bbed will respondshowing the current block. --注意这里的block 是一个相对的位置,我们需要先指定一个file,然后在指定block。 即对应file里的block。可以对当前block的位置进行+和-操作。 BBED> set file 4 FILE# 4 BBED> set block 60882 BBED-00309: out of range block number(60882) BBED> set file 1 FILE# 1 BBED> set block 60882 BLOCK# 60882 BBED> set bock +10 BBED-00202: invalid parameter (bock) BBED> set block +10 BLOCK# 60892 BBED> set block -10 BLOCK# 60882 BBED> set file 4 block 520 FILE# 4 BLOCK# 520 BBED> set dba 4,520 DBA 0x01000208 (16777736 4,520) 二.1.5 set offset Sets the current offset. The offset is relative to the block already set. Theabsolute offset can be specified, or an offset to the current offset can bespecified using the plus (+) or minus (-) symbols. If successful, bbed willrespond showing the current offset. --偏移量是相对某个block里的偏移量,可以用+和-进行操作 BBED> set offset 20 OFFSET 20 BBED> set offset +2 OFFSET 22 BBED> set offset -2 OFFSET 20 二.1.6 set blocksize Sets the blocksize of the current file. The blocksize must match the file selectedor an error will be reported. If successful, bbed will respond showing thecurrent blocksize. 设置当前datafile 的blocksize 大小,该大小必须和datafile 的实际block 匹配,否则会报错。 BBED> set blocksize 8192 BLOCKSIZE 8192 二.1.7 set listfile Sets the listfile to the specified file. This option can be used if the listfile wasnot specified on the command line. The listfile must be enclosed in singlequotes. If successful, bbed will respond showing the current listfile. --在前面讲过,可以通过parameter file 来指定bbed的属性,当然也可以通过set 来指定这些信息。对于listfile的文件,必须用单引号括起来。 BBED> set listfile '/u01/filelist.txt' LISTFILE /u01/filelist.txt 二.1.8 set width Sets the current screen width. If not specified bbed will assume an 80-characterdisplay. 设定当前屏幕的宽度,默认是80. BBED> set width 200 WIDTH 200 二.1.9 set count Sets the number of bytes of the data block to display from the dump command. Thedefault is 512. Tosee an entire 8Kb block therefore you would need to dump the block eight timesat offsets 0, 512, 1024, 1536, 2048, 2560, 3092 and 3604. By setting the count higher bbed will dump more of the block each time. Byreducing it a smaller dump can be achieved. 设置dump 命令显示bytes的数量。默认是512 bytes。 BBED> set count 512 COUNT 512 二.1.10 set ibase Sets the internal number base. The default is decimal. However it can also be set tohexadecimal or octal. This allows the set file, set block and set offsetcommands to use an alternate base to decimal. If successful, bbed will respondshowing the current base: --设置内部的数字格式,默认是十进制。 也可以设置为十六进制或者八进制。设置完数字格式之后,可是使用该格式来设置blcok,offset等。 BBED> set ibase hex IBASE Hex BBED> set block +D BLOCK# 14 BBED> set ibase decimal IBASE Dec 二.1.11 set mode Sets the bbed mode. The options are browse or edit. In browse mode no changes can bemade. This is the suggested mode for first-time users, or if you are intendingto use the tool only to inspect data blocks. --设置bbed 的模式,该默认有2种:browse 和 edit。 browse 模式不允许进行修改。 如果要修改,就选择edit模式。 这个在我们的之前的配置文件里,我们选择了edit。 BBED> set mode browse MODE Browse BBED> set mode edit MODE Edit 二.2 show 命令 显示当前的配置选项。 show |

|
|
BBED> show FILE# 1 BLOCK# 14 OFFSET 0 DBA 0x0040000e(4194318 1,14) --注意这里的block 变成了14. 是我们刚才设置的。 FILENAME /u01/app/oracle/oradata/dave2/system01.dbf BIFILE bifile.bbd LISTFILE /u01/filelist.txt BLOCKSIZE 8192 MODE Edit EDIT Unrecoverable IBASE Dec OBASE Dec WIDTH 200 COUNT 512 LOGFILE log.bbd SPOOL No 二.3 info 显示当前可以进行browse 或者edit 的file。即我们filelist 里指定的datafile信息。 Info |
|
|
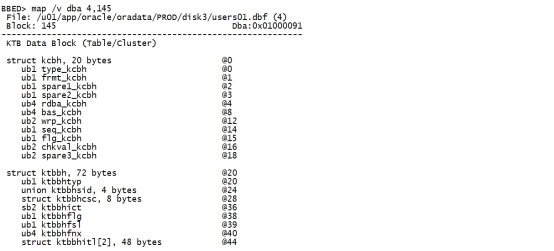
二.4 map The map command shows a map of the current block. It can be combined with the /voption to produce a more verbose output. The map shows the offsets throughout the block where certain information can be found such as the block header, the data block header or the row directory. If the set commands have not been used to set a current block, or it the user simply wishes to examine another block while keeping the current block their focus,the file name, file id, block or DBA can be specified with the command. Map会通过偏移量来显示block里的详细信息,如block header,data block header 和row directory。 使用/v 选项,可以查看更详细的信息。 在不指定block的情况下,会显示当前block的信息,如果想显示其他block的信息,可以使用file name,file id,block 和DBA 来指定要显示的block。 --通过dba 来指定某个block map /v dba 4,145 |
|
|
|
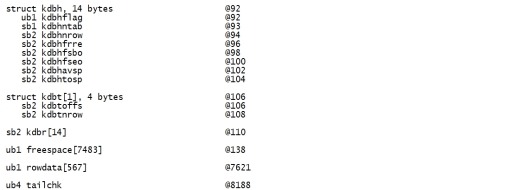
Map 显示的具体信息解释如下: struct kcbh, 20 bytes Block Header Structure ub1 type_kcbh Block type (see Header Block Types below) ub1 frmt_kcbh Block format 1=Oracle 7, 2=Oracle 8+ ub1 spare1_kcbh Not used ub1 spare2_kcbh Not used ub4 rdba_kcbh RDBA -Relative Data Block Address ub4 bas_kcbh SCN Base ub2 wrp_kcbh SCN Wrap ub1 seq_kcbh Sequence number, incremented for every change made to the block at the same SCN ub1 flg_kcbh Flag: 0x01 New Block 0x02 Delayed Logging Change advanced SCN/seq 0x04 Check value saved - block XOR‘s to zero 0x08 Temporary block ub2 chkval_kcbh Optional block checksum (if DB_BLOCK_CHECKSUM=TRUE) ub2 spare3_kcbh Not used struct ktbbh, 72 bytes Transaction Fixed Header Structure ub1 ktbbhtyp Block type (1=DATA, 2=INDEX) union ktbbhsid, 4 bytes Segment/Object ID struct ktbbhcsc, 8 bytes SCN at last block cleanout b2 ktbbhict Number of ITL slots ub1 ktbbhflg 0=on the freelist ub1 ktbbhfsl ITL TX freelist slot ub4 ktbbhfnx DBA of next block on the freelist struct ktbbhitl[2], 48 bytes ITL list index struct kdbh, 14 bytes Data Header Structure ub1 kdbhflag N=pctfree hit(clusters); F=do not put on freelist; K=flushable cluster keys b1 kdbhntab Number of tables (>1 in clusters) b2 kdbhnrow Number of rows sb2 kdbhfrre First free row entry index; -1 = you have to add one sb2 kdbhfsbo Freespace begin offset sb2 kdbhfseo Freespace end offset b2 kdbhavsp Available space in the block b2 kdbhtosp Total available space when all TXs commit struct kdbt[1], 4 bytes Table Directory Entry Structure b2 kdbtoffs b2 kdbtnrow sb2 kdbr[1] Row Directory ub1 freespace[8030] Free Space ub1 rowdata[38] Row Data ub4 tailchk (See Tailchecks below) Different block types are designated by the first byte of the block. The following tableshows how to decode the block type: 不同的block 可以第一个byte的值是不一样的。 具体值对应block 类型如下。 Header Block Types ID Type 01 Undo segment header 02 Undo data block 03 Save undo header 04 Save undo data block 05 Data segment header (temp, index, data and so on) 06 KTB managed data block (with ITL) 07 Temp table data block (no ITL) 08 Sort Key 09 Sort Run 10 Segment free list block 11 Data file header 可以通过dump block来查看对应的具体的值。 下文讲dump时会有相关的示例。 oracleblocks 的最后4个bytes 是tail check。 下面看一下oracle 9i block的tail check 组成。 Tailchecks Thetail of an Oracle 8+ block is a concatenation of the lower order two bytes ofthe SCN base, the block type and the SCN sequence number. Oracleblock tail 由4个bytes组成,但实际上只用了低2个bytes来存放。 2个bytes的tail 由scn base,block type 和 scn sequence 组成。 E.g, if the SCN base number is 0x00029728,the block type is 06 and the SCN sequence number is 0x02, the tail check wouldbe 0x97280602: SCN base Type SCN seq 9728 06 02 Althoughthis tail check value is generated from three components, Oracle treats thefinal value as a single unsigned integer stored as a word (4-bytes). Onlittle-endian architecture machines, which include Intel, the value will bestores as low-order byte first. 虽然tail check 由3个部分组成,但是oracle 把这3部分作为一个整体来存储,并且占用4个bytes。 对于little-endian(低端)架构的机器,包括Intel, 他们会先存放low-order byte,即低位字节。 Thereforeif the tail check is examined in the block using a standard block editor, orthe dump command which will be explained in the next section, the byte ordermay look different. A tail check of 0x97280602 stored on an Intel machine wouldbe written to disk as "02062897". 可以通过标准block editor 或者dump 来查看tail check。 对于不同的机器,他们存储的顺序是不一样的。比如tail check 0x97280602 在Intel Machine 就被存储为02062897,因为它会先保存low-order bytes。 二.5 dump(d) The dump command dumps the content of the block to the screen. It can be combinedwith the /v option to produce a more verbose output. TheDBA, Filename, File, Block and/or Offset to dump can be specified with thecommand. If these are not specified the current file, block and offsetas established with the set command will be dumped. The size of the dump islimited by the set count option and defaults to 512 bytes or alternatively thesize of the dump can be specified with the command. dump命令可以将block 的内容显示到屏幕。 每次显示的bytes由count 控制,默认是512 bytes。 使用 /v 选项,可以显示更多详细信息。 dump /v dba 4,145 offset 0 count 128 |
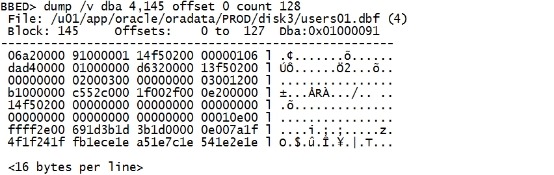
|
|
二.6 examine(x) The examine command is used to display data from the block in raw or formattedoutput. The DBA, Filename, File, Block and/or Offset to examine can bespecified with the command. If these are not specified the current file, blockand offset as established with the set command will be examined. If the examinecommand is issued with just the block and offset to examine, bbed will displaythe data structure at that offset. --examine命令也是用来显示datablock的内容的。 Unlikethe print command it cannot interpret data structures, but it can be used todisplay row information. Combined with knowledge of the data type of the row,it can be used to retrieve complete rows from the block: --print命令不能对data structures 进行一个解释说明。 The examine command will interpret the data in the block according to the followingswitches: Switch Display Format /b b1, ub1 (byte) /h b2, ub2 (half-word) /w b4, ub4 (word) /l b8, ub8 (long) (was b4/ub4 in Oracle7). /r Oracle table/index row Theexamine command allows switches from the print command to be combined withthese specific switches to interpret data. --examine可以根据switch的方式和print 命令进行一个结合来对data 进行解释说明。 Forexample if we wanted to interpret data as an Oracle table row with the firstcolumn character and the second and third columns numeric, we would execute thecommand as follows: BBED>x /rcnn Thefollowing example shows the print and examine commands being used to step throughthe first and second rows of a block, with the data interpreted as a row in theformat: character, number, number: x /rcnn |
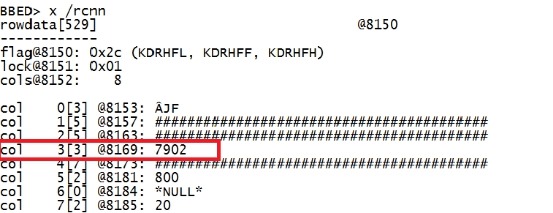
|
|
select * from scott.emp; |
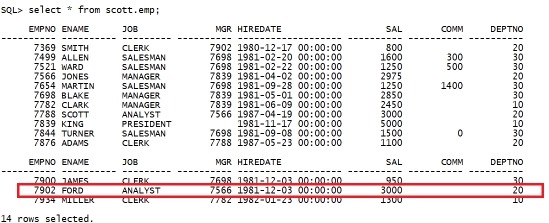
|
|
二.7 find(f) The find command is used to locate data within a block. The command allows hex,string or numeric data to be searched for. The pattern can be searched for fromthe top of the block (offset 0) using the TOP directive, or from the currentposition using the CURR directive. find命令可以用来搜索关键字。 可以从offset 0 搜索到top 或者从当前的offset 搜索到top。 Switchesare used to determine the data type of the pattern to search for. These areshown below: Switch Datatype /x Hexadecimal /d Decimal /u unsigned decimal /o Octal /c character (native) Note: Number and Dates are not supported bythe find command. find 命令支持的switch 类型如上表,注意,find 不支持number和Date 。 select rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid)rel_fno, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid)blockno, dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) rowno from scott.emp; |
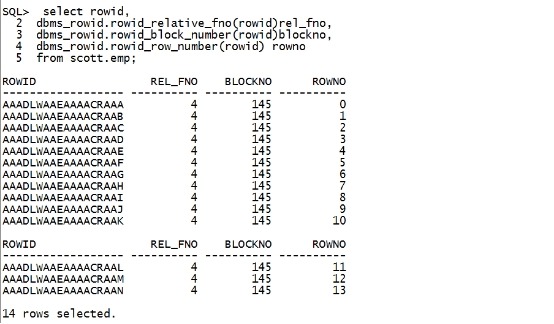
|
|
set file 4 set block 145 set offset 0 find /c SCOTT top |
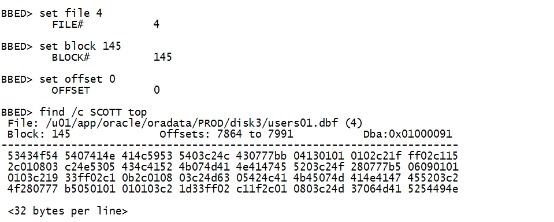
|
|
d /v dba 4,145 offset 7864 count 128 |
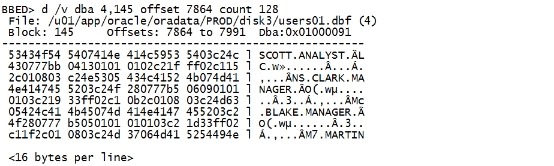
|
|
SCOTT 二.8 copy The copy command is used to copy blocks from one location to another. As with other commands, the file or filename and offset can be specified, or the DBA can be specified instead. 可以把一个块的内容拷贝到另一个块中。 命令格式如下: BBED> copy dba 1,115362 to dba 1,115363 copy 是个危险的命令,慎用。 二.9 modify(m) BBED> help modify MODIFY[/x|d|u|o|c] numeric/character string [ DBA | FILE | FILENAME | BLOCK | OFFSET | symbol | *symbol ] BBED> The modify command is used to change data inside a block. The DBA, Filename, File,Block and/or Offset to modify can be specified with the command. If these are not specified the current file, block and offset as established with the set command will be modified. Alternatively a symbol or symbol pointer can bespecified for modification. The pattern of bytes used to overwrite the original can be specified inhexadecimal, decimal, unsigned decimal, octal or character data using the sameswitches as the find command. 可以修改块中的内容,该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 在file 1,block 115362 有我们的Dave,我们这里把Dave 改成dmm。 modify /c HAHAH dba 4,31 offset 7864 该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |
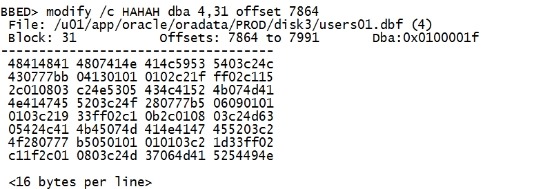
|
|
d /v dba 4,31 offset 7864 count 128 |

|
|
select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
现在无改变。 sum apply |

|
|
重启库才能生效。 shutdown immediate; startup select * from scott.emp; |
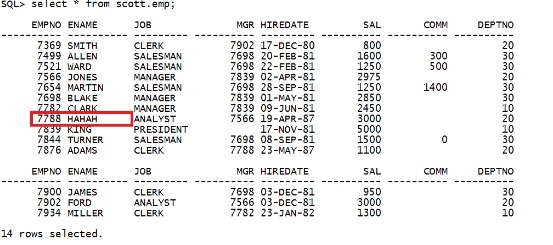
|
|
二.10 assign The assign command does symbolic assignment, with type and range checking. Either target or source can be omitted for the current offset. For example, the following command assigns structure at current offset to file 4,block 2 ”s first ITL entry BBED> assign dba 4, 145 ktbbhitl[0] 指定结构 ,不演示。 二.11 sum Thesum command is used to check and set the block checksum. The DBA, Filename,File, Block and/or Offset to check can be specified with the command. If theseare not specified the current file, block and offset as established with theset command will be checked. Theapply directive can be used to update the checksum. 我们可以使用bbed 对block 进行修改。 要使这些修改生效,就要使用sum命令。 该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 sum dba 4,31 apply 该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |

|
|
重启库或清除缓冲区才能生效。 二.12 push / pop Thepush and pop commands are used to push a file, block and offset location onto amemory backed stack and then pop them back. This allows a current locationbeing edited to be temporarily saved while another location is examined ormodified. Note that the stack only stores the location? it does notsave the contents. --push命令将对象放到内存的stack,pop 将对象从内存写回磁盘。 Thefollowing example shows file 7, block 16, offset 8163 being examined. Thelocation is saved with the push command. We then move to file 6, block 1 beforereturning to DBA 7,16 with the pop command. BBED> push dba 7,16 DBA 0x01c00010 (29360144 7,16) OFFSET 8163 BBED> set dba 6,1 DBA 0x01800001 (25165825 6,1) BBED> pop DBA 0x01c00010 (29360144 7,16) OFFSET 8163 The command pop all can be used to remove all push‘d entries from the stack. Thecommand show all can be used to show all saved locations. 二.13 revert Therevert command is used to restore a file, filename, block or DBA to it‘soriginal state when bbed was started. revert是恢复自bbed 启动以来的所有修改。 revert dba 4,31该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |

|
|
sum dba 4,31 apply |
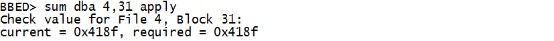
|
|
重启库才能看到变化。 shutdown immediate startup |
|
|
或者: alter system flush buffer_cache; |

|
|
select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
还是没有改变,flush 一下buffer cache之后就更改回来了。我们刚才在之前的测试时,是重启了DB。 看来也是启了flush buffer cache的作用。 二.14 undo Theundo command rolls back the last modify or assign command. If the undo commandis issued again the modification is re-done. undo命令是回滚最后一次的操作。 该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 modify /c HAHAH dba 4,31 offset 7864该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |
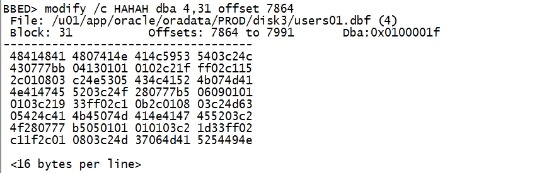
|
|
d /v dba 4,31 offset 7864 count 128 |
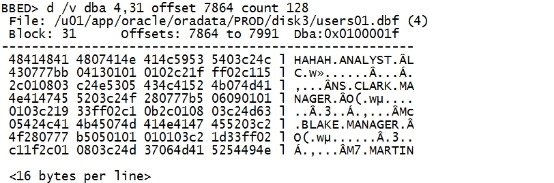
|
|
sum apply |

|
|
一定要提交。 如果不提交之前可以 undo 该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |
|
|
alter system flush buffer_cache; |

|
|
select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
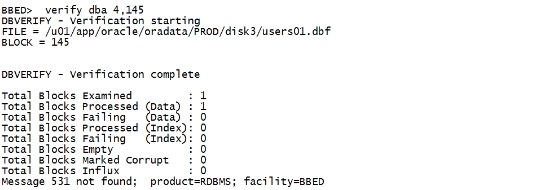
二.15 verify Theverify command is used to verify the integrity of the block. It performs asimilar function to the dbverify utility. verify命令用来验证block的完整性。 verify dba 4,145 |
|
|
查看有没有坏块 二.16 corrupt The corrupt command is used to mark blocks as media corrupt. corrupt命令将一个block 标记为corrupt,这样db 在操作时就会跳过该block,从而避免错误。 verify dba 4,31 该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |

|
|
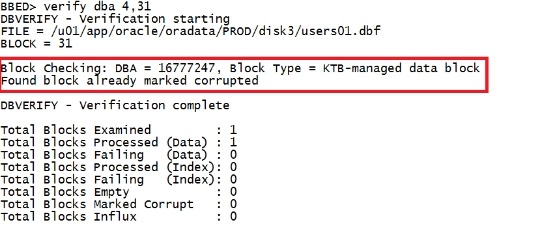
corrupt dba 4,31该步骤不演示,下面实验有。 |

|
|
verify dba 4,31 |
|
|
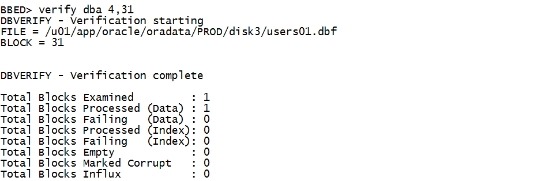
注意: undo 命令不能undo 一个corruption,但是revert 命令却可以。 revert dba 4,31 |

|
|
sum apply |

|
|
verify dba 4,31 |
|
|
二.17 修改数据块中的内容 本例综合运用上面的各种命令,修改块的内容,并撤销修改。 在sqlplus中操作 select * from scott.emp; |
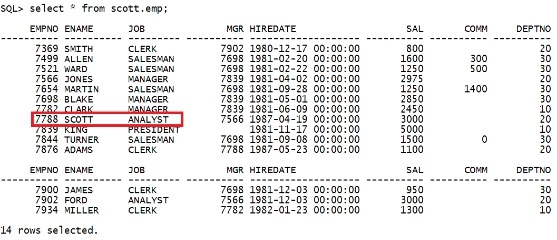
|
|
现在无改变。 select rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid)rel_fno, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid)blockno, dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) rowno from scott.emp; |
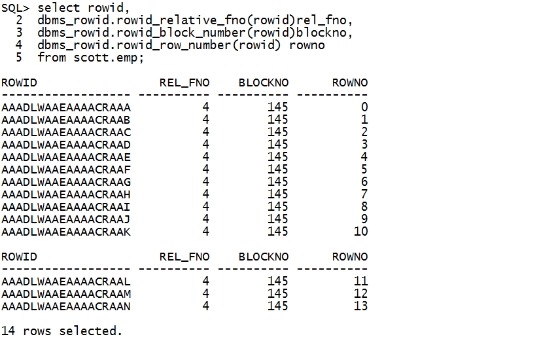
|
|
在bbed中操作 set dba 4,145 offset 0 find /c SCOTT top |
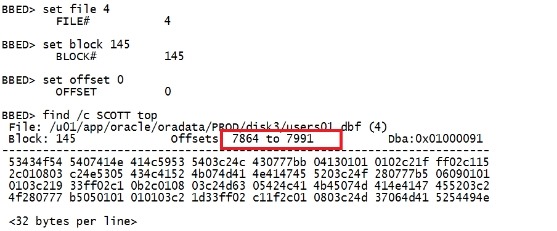
|
|
dump /v dba 4,145 offset 7864 count 128 |
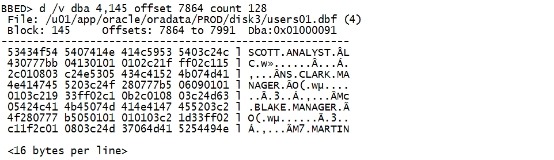
|
|
注意这里面的Offsets:7864 to 7991, 它指的是这一行的一个地址。其中 S 的offset 是7864 C 的offset 是7865 O 的offset 是7866 T 的offset 是7867 空格也算offset。 modify /c HAHAH dba 4,145 offset 7864 |
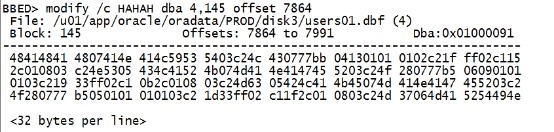
|
|
sum apply |

|
|
或者 sum dba 4,145 apply |

|
|
dump /v dba 4,145 offset 7864 count 128 |
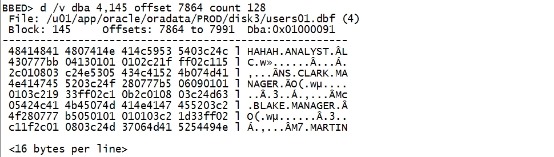
|
|
在sqlplus中操作 alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
二.17.1 下面撤销修改: 在bbed中操作 revert dba 4,145 |

|
|
sum dba 4,145 apply |
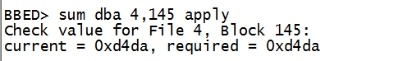
|
|
在sqlplus中操作 alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
二.18 恢复delete的rows When rows are deleted in Oracle the data is not actually removed. The row is simply marked as deleted and the free space counters and pointers adjusted accordingly. The status of a row is stored in the Row Header which occupies the first few bytes of each row. 当row 被delete 的时候,实际上data 并没有被remove,只是将该row 标记为delete,然后其对应的空间被统计为free space。 row 的status 存在每个row的row header里。 The Row Header consists of the Row Flag, Lock Byte (ITL entry) and Column Count.The first of these - the Row Flag - is a single byte that holds a bitmask thatshows the status of the row. The bitmask is decoded as follows: RowHeader 包含Row Flag,Lock Byte(ITL)和column Count。其中Row Flag占用1个byte,并且以bitmask 来保存。bitmask 的解释如下: Cluster Key Cluster Table Member Head of row piece Deleted First data piece Last data piece 1st Column continues from previous piece Last column continues in next piece 128 64 32 16 8 4 2 1 二.18.1 删除前 在sqlplus中操作 select * from scott.emp; |
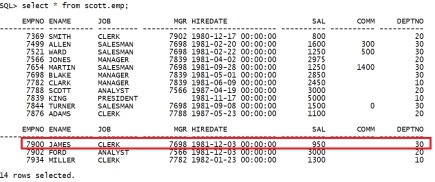
|
|
select rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid)rel_fno, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid)blockno, dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) rowno from scott.emp; |

|
|
col segment_name for a10 select extent_id,segment_name,bytes/1024 k,file_id,block_id from dba_extents where owner='SCOTT'; |
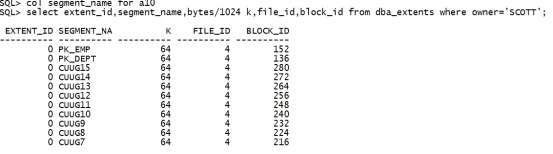
|
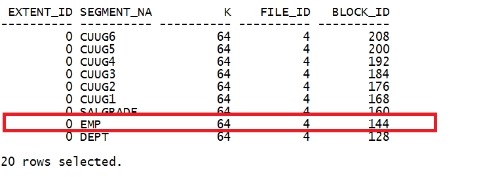
|
|
alter system checkpoint; |

|
|
alter system dump datafile 4 block 145; |

|
|
查询dump到哪个trace文件中: oradebug setmypid oradebug tracefile_name |

|
|
more /u01/app/oracle/oradata/PROD/dump/diag/rdbms/prod/PROD/trace/PROD_ora_6241.trc 可以看到这个表有14条记录。 |
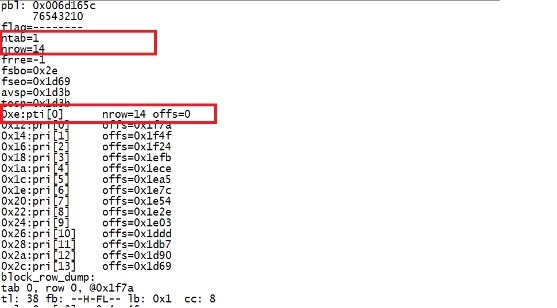
|

|
|
注意这里的fb: --H-FL--。 其有8个选项,每个值分别与bitmask 对应。 Therefore,columns that fit within a single block, are not chained, migrated or part of aclustered table and are not deleted will have the following attributes: (1)Head of Row Piece (2)First Data Piece (3)Last Data Piece 如果一个row 没有被删除,那么它就具有上面的3个属性,即Flag 表示为:--H-FL--. 这里的字母分别代表属性的首字母。其对应的值:32 + 8 + 4 =44 or 0x2c. 如果一个row 被delete了,那么row flag 就会更新,bitmask 里的deleted 被设置为16. 此时row flag 为: 32 + 16 + 8 + 4 = 60 or 0x3c. delete from scott.emp where empno=7900; commit; select * from scott.emp; |

|

|
|
二.18.2 删除后 alter system checkpoint; alter system dump datafile 4 block 145; |
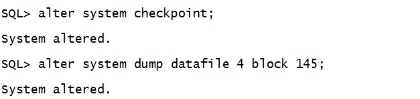
|
|
查询dump到哪个trace文件中: oradebug setmypid oradebug tracefile_name |

|
|
more /u01/app/oracle/oradata/PROD/dump/diag/rdbms/prod/PROD/trace/PROD_ora_6241.trc |
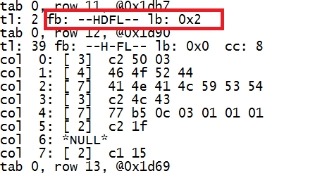
|
|
注意上面的标签被删除的数据是HDFL,一般是H-FL。 现在我们用bbed 将删除的内容找回来。 在bbed中操作 set dba 4,145 offset 0 find /c JAMES top |
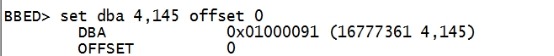
|

|
|
dump /v dba 4,145 offset 7706 count 128 |
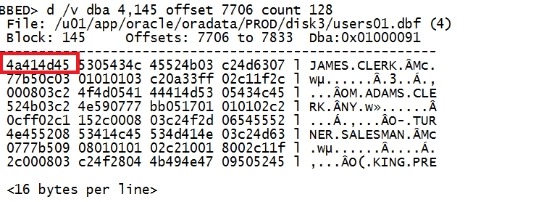
|
|
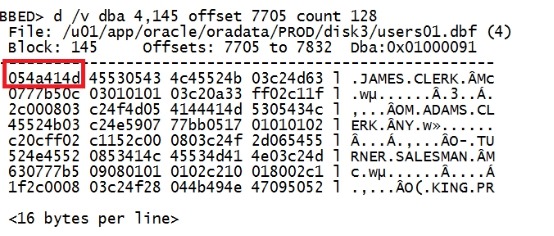
d /v dba 4,145 offset 7705 count 128 |
|
|
比刚刚多了两个字符。 8个字符才是一个完整的信息,所以要改变4个偏移量才能展示完整的信息。 7706-8=7698,再加1=7699. 寻找原则:和row directory核对,寻找前面最接近的值。 d /v dba 4,145 offset 7699 |
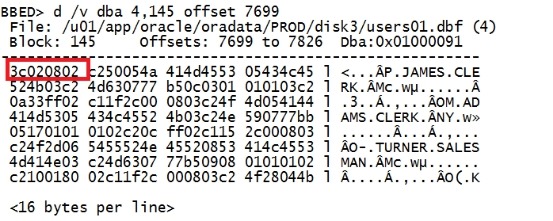
|
|
这里已经出现了我们3c(deleted)标志,但是注意这里的位置的根据我们的查找的字符串来分的,实际在block里的分割方式不一样按照我们的offset 来进行。 我们可以通过row directory 来进行一个确认。 验证一下 p kdbr |

|
|
p *kdbr[9] p *kdbr[10] p *kdbr[11] p *kdbr[12] |

|
|
确定7699就是3c的开头。 modify /x 2c offset 7699 |
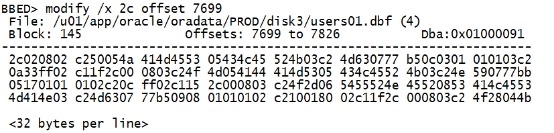
|
|
sum apply |
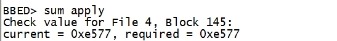
|
|
在sqlplus中操作 alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.emp; |
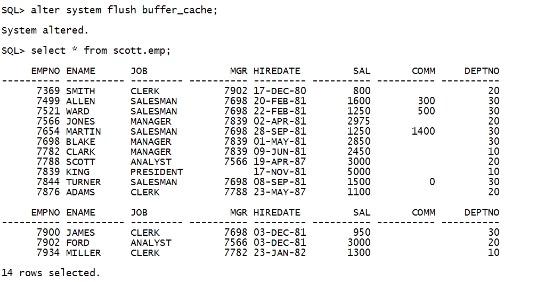
|
|
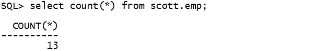
之前delete 的数据已经恢复出来。 但是: 系统认为已经删掉了。 select count(*) from scott.emp; |
|
|
alter table scott.emp move; |

|
|
二.19 使用copy命令从旧数据文件中恢复delete的rows 将表scott.emp移动到我们的单独的datafile里(目的是查找清晰,并恢复上面的破坏): col tablespace_name for a15 select tablespace_name,contents,status from dba_tablespaces; |

|
|
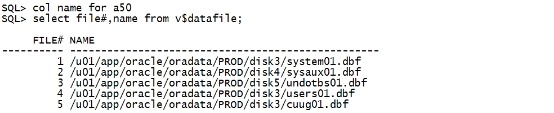
col name for a50 select file#,name from v$datafile; |
|
|
create tablespace lxtbs datafile '/u01/app/oracle/oradata/PROD/disk3/lxtbs01.dbf' size 50m; |

|
|
alter table scott.emp move tablespace lxtbs; alter index scott.pk_emp rebuild tablespace lxtbs; |

|
|
col table_name for a10 select table_name,tablespace_name,blocks from dba_tables where owner='SCOTT'; |

|
|
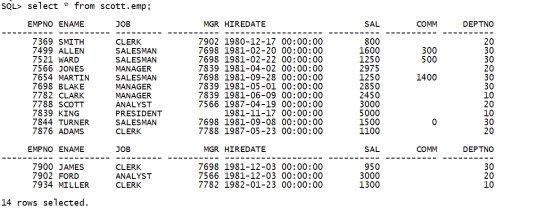
select * from scott.emp; |
|
|
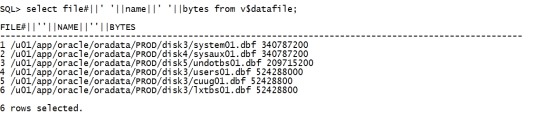
select file#||' '||name||' '||bytes from v$datafile; |
|
|
二.19.1 创建一个旧的数据文件 shutdown immediate; |
|
|
关库后再操作: cp /u01/app/oracle/oradata/PROD/disk3/lxtbs01.dbf /home/oracle cd /home/oracle ls |
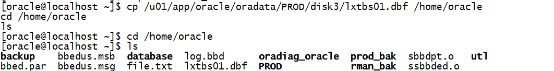
|
|
将copy 的bak datafile 添加到bbed 的parfile里面 vi file.txt 添加: 6 /u01/app/oracle/oradata/PROD/disk3/lxtbs01.dbf 52428800 7 /home/oracle/lxtbs01.dbf 52428800 |
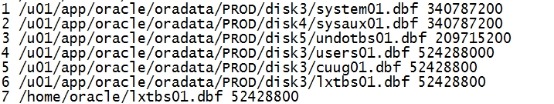
|
|
最后的7号文件是我们添加的。 startup |
|
|
select rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid)rel_fno, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid)blockno, dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) rowno from scott.emp; |
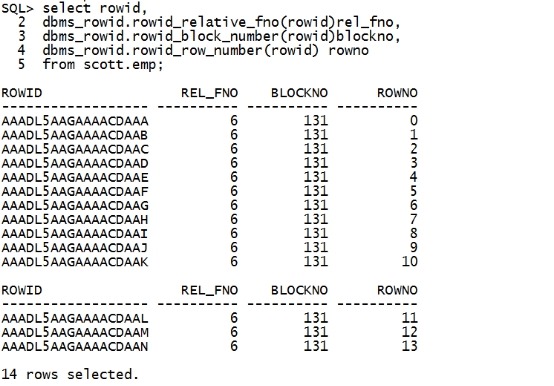
|
|
col owner for a10 col segment_name for a10 select owner,segment_name,header_file,header_block,blocks from dba_segments where owner='SCOTT'; |
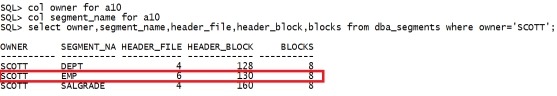
|
|
从这个查询结果,我们可以看到,对象保存在datafile 6里,从130 的block 开始存储,占用8个blocks。 这里要注意的一点是:dba_segments 视图里的block 是从0开始的统计的,而bbed 里是从1. 所以我们在bbed中指定block时,需要加1(130会报错),也就是131 quit bbed parfile=/home/oracle/bbed.par blockedit |

|
|
下面能查出东西来就行。 set dba 6,130 offset 0 p ktbbh |
|
|
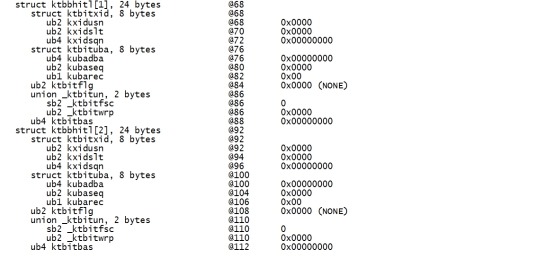
set dba 6,131 offset 0 p ktbbh |

|
|
|
做一个误删除操作: delete from scott.emp; commit; select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
二.19.2 使用copy 从旧的datafile里恢复 set width 70 info |
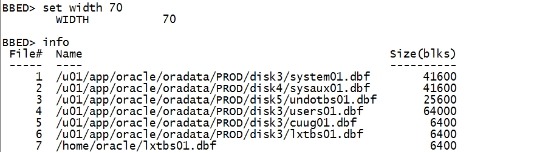
|
|
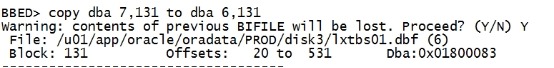
其中7是我们的旧的数据文件。 copy dba 7,131 to dba 6,131 |
|
|
copy剩下的7个块: copy dba 7,132 to dba 6,132 copy dba 7,133 to dba 6,133 copy dba 7,134 to dba 6,134 copy dba 7,135 to dba 6,135 copy dba 7,136 to dba 6,136 copy dba 7,137 to dba 6,137 copy dba 7,138 to dba 6,138 sum apply |

|
|
alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.emp; |

|
|
如果出不来就再做一遍copy,数据就回来了,或者重启db数据也能回来。 但是: select count(*) from scott.emp; |

|
|
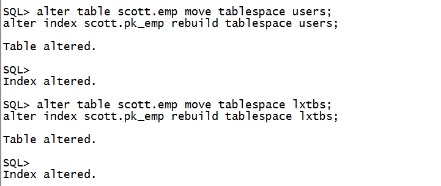
需要再move一次。 alter table scott.emp move tablespace users; alter index scott.pk_emp rebuild tablespace users; alter table scott.emp move tablespace lxtbs; alter index scott.pk_emp rebuild tablespace lxtbs; |
|
|
select count(*) from scott.emp; |

|
|
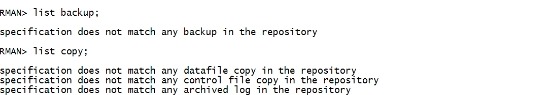
二.20 坏块恢复(Rman Blockrecover) 有些人喜欢用bbed干一些弄简为繁的事情,比如控制文件丢失,或者介质故障开不了库,手工修改scn号开库,或坏块修复等。如果不是高手,最好不要用bbed进行高风险的工作,其实Oracle Rman提供了修复坏块的工具block recover。但前提条件是你得有一个可用的备份存在。 最好重新做一次备份: rman target / delete noprompt backup; delete noprompt copy; list backup; list copy; |
|
|
run{ shutdown immediate; startup mount; allocate channel c1 type disk; allocate channel c2 type disk; backup database format '/home/oracle/rman_bak/cold_bak/%d_%s_%p.bak'; alter database open; } |

|
|
run{ sql 'alter system switch logfile'; allocate channel c1 type disk; allocate channel c2 type disk; backup database format '/home/oracle/rman_bak/hot_bak/%d_%s_%p_hot.bak' filesperset 3; sql 'alter system switch logfile'; } |
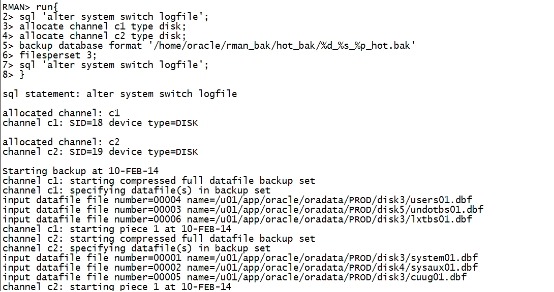
|
|
/************************重新登录*************************/ sqlplus重新登录: quit sqlplus '/as sysdba' bbed重新登录 quit bbed parfile=/home/oracle/bbed.par blockedit /************************重新登录*************************/ 二.20.1 制作坏块 先用bbed搞坏数据块。 select rowid, dbms_rowid.rowid_relative_fno(rowid)rel_fno, dbms_rowid.rowid_block_number(rowid)blockno, dbms_rowid.rowid_row_number(rowid) rowno from scott.dept; |
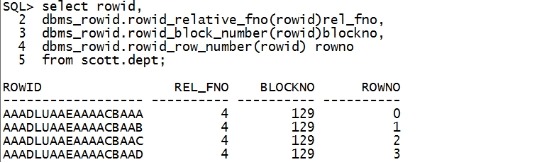
|
|
col segment_name for a10 select owner,segment_name,header_file,header_block,blocks from dba_segments where owner='SCOTT'; |
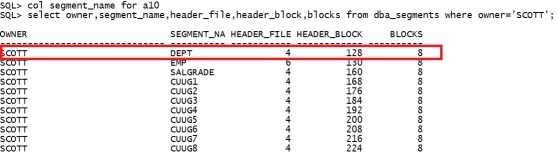
|
|
加一变成129. set dba 4,128 offset 0 p ktbbh |

|
|
set dba 4,129 offset 0 p ktbbh |
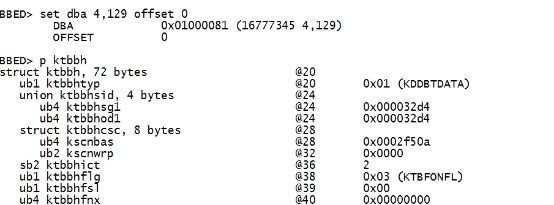
|
|
map |
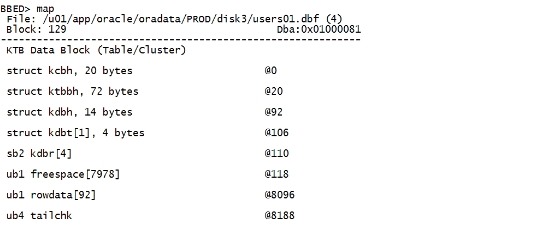
|
|
d /v offset 0 count 128 |
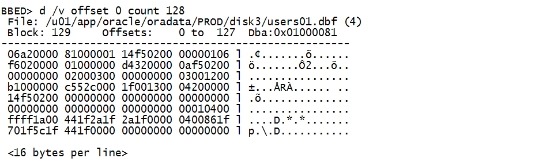
|
|
modify /x 12345678 offset 0 单步执行,或copy命令制作坏块 sum apply |
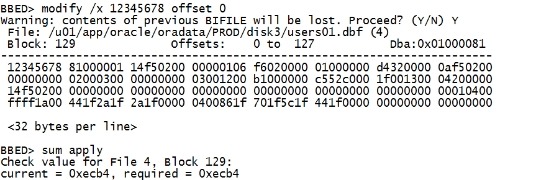
|
|
d /v offset 0 count 128 |

|
|
alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.dept; |
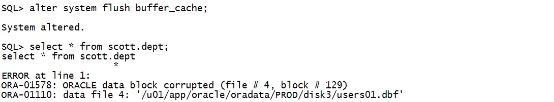
|
|
--当Oracle 认为一个block 是corrupt时,会将该block的sequence number 标记为0xff. 该值可以通过seq_kcbh 属性查看。 set dba 4,129 p kcbh |
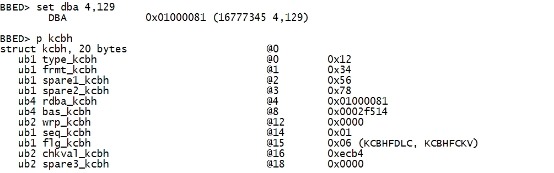
|
|
verify dba 4,129 |
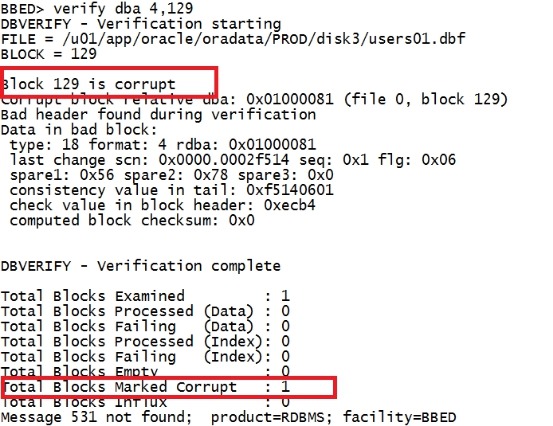
|
|
二.20.2 恢复坏块 不建议使用bbed来操作,rman有工具可以很好的处理,bbed做的话就是revert回去就好了。 BBED> revert All changes made in this session will be rolled back. Proceed? (Y/N) Y Reverted file '/oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/users01.dbf', block 520 Reverted file '/oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/users01.dbf', block 523 Warning: contents of previous BIFILE will be lost. Proceed? (Y/N) Y 下边来尝试rman恢复: rman target / |

|
|
不要执行:只适用于一两个坏块 blockrecover datafile 4 block 129,130; 如果有多个坏块,最好先校验: backup validate datafile 4; |
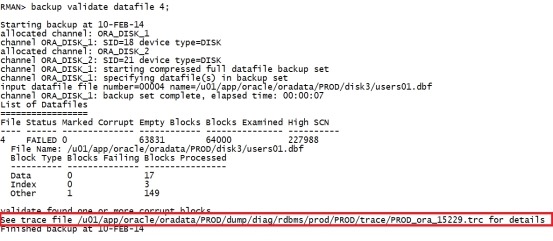
|
|
select * from v$database_block_corruption; |
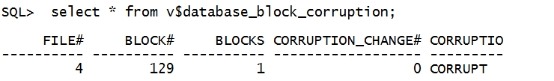
|
|
修复全部坏块。 blockrecover corruption list; |
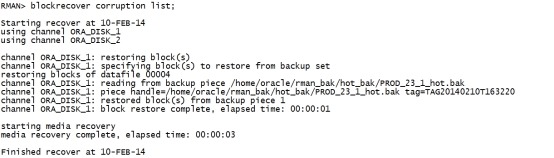
|
|
alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.dept; |
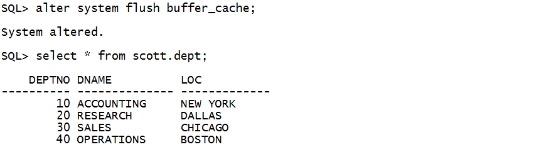
|
|
用rman的备份,修复了这个块。 select * from v$database_block_corruption; |

|
|
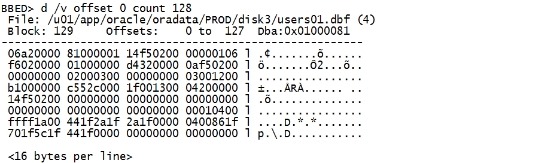
set dba 4,129 d /v offset 0 count 128 |

|
|
|
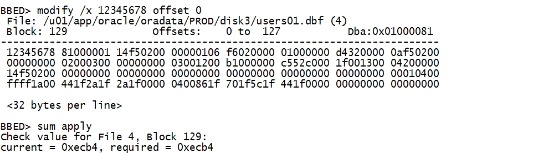
二.20.3 坏块的影响 再次搞坏数据块: set dba 4,129 d /v offset 0 count 128 modify /x 12345678 offset 0 sum apply |
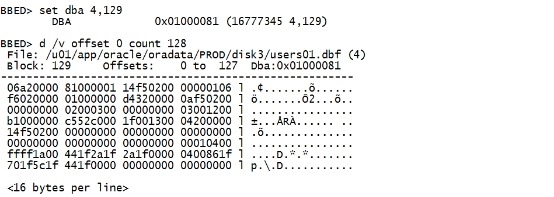
|
|
|
alter system flush buffer_cache; select * from scott.dept; |
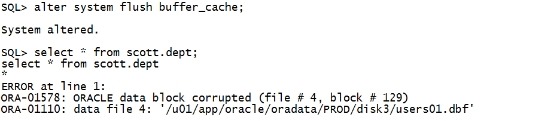
|
|
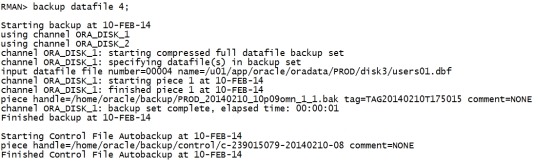
rman内操作: backup datafile 4; |
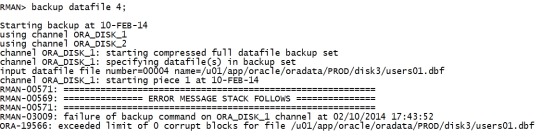
|
|
RMAN> backup datafile 4; Starting backup at 2016-04-06 14:25:42 using channel ORA_DISK_1 channel ORA_DISK_1: starting full datafile backup set channel ORA_DISK_1: specifying datafile(s) in backup set input datafile file number=00004 name=/oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/users01.dbf channel ORA_DISK_1: starting piece 1 at 2016-04-06 14:25:42 RMAN-00571: =========================================================== RMAN-00569: =============== ERROR MESSAGE STACK FOLLOWS =============== RMAN-00571: =========================================================== RMAN-03009: failure of backup command on ORA_DISK_1 channel at 04/06/2016 14:25:45 ORA-19566: exceeded limit of 0 corrupt blocks for file /oracle/app/oracle/oralhr/users01.dbf col tablespace_name for a10 col owner for a10 col owner for a10 col PARTITION_NAME for a10 SELECT tablespace_name,segment_type,owner,segment_name,partition_name FROM dba_extents WHERE file_id = &file_id AND &block_id BETWEEN block_id AND block_id+blocks-1; 输入: 4 129 |
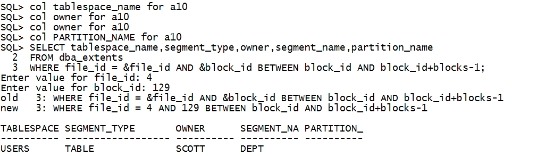
|
|
run{ set maxcorrupt for datafile 4 to 2; backup datafile 4 tag='2corruptblock'; } |
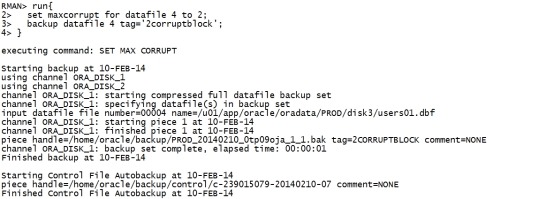
|
|
这样才能备份,但是推荐先修复坏块: backup validate datafile 4; |
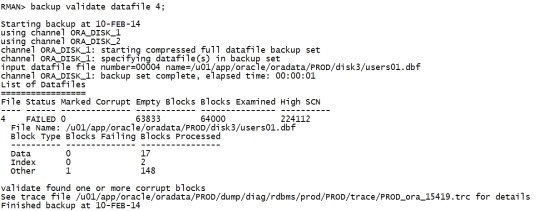
|
|
blockrecover corruption list; |
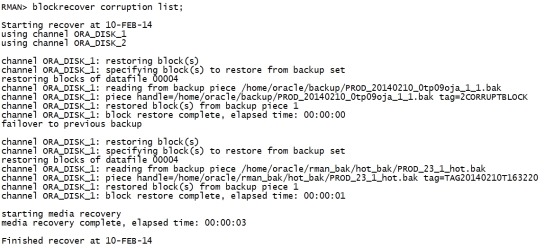
|
|
backup datafile 4; |